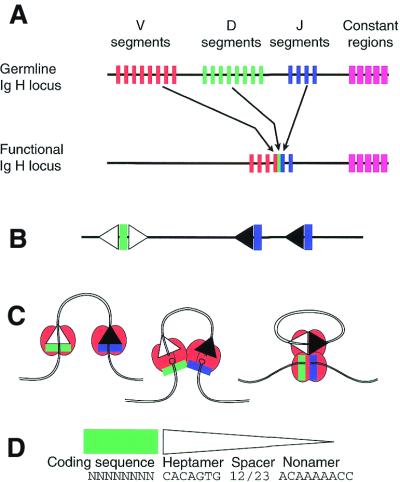
Figure 1.
1 The V(D)J recombination reaction scheme. (A) The colored bars represent the tandemly-arranged clusters of coding DNA segments at the Ig heavy chain locus of the mouse. There are actually several hundred V segments, many of which are pseudogenes. One of each of the V, D and J elements are joined to form the functional coding region that encodes the variable portion of the molecule, as shown. Junctional diversity is introduced at each event (see text). The constant regions do not participate in V(D)J joining. (B) Each of the coding segments is associated with an RSS, which specifies the recombination cleavage site. White triangles represent 12-RSS, black triangles represent 23-RSS. Since D elements participate in both upstream and downstream recombination events, they require two RSSs. (C) The conventional reaction course involves RAG proteins (red, stoichiometry not implied) associating at the RSS. Cooperative cleavage generates blunt signal ends on the RSS and hairpinned intermediates on the coding ends. Coding ends are processed and the four ends are then rejoined, signal-containing ends to each other, and similarly for coding ends (see text). (D) The sequence of the coding end is not highly constrained, although some sequences at the cleavage site work better than others. The consensus RSS (triangle) is composed of a conserved heptamer, a spacer of either 12 or 23 nt in length and a conserved nonamer. Some variation in each of these motifs can be tolerated.