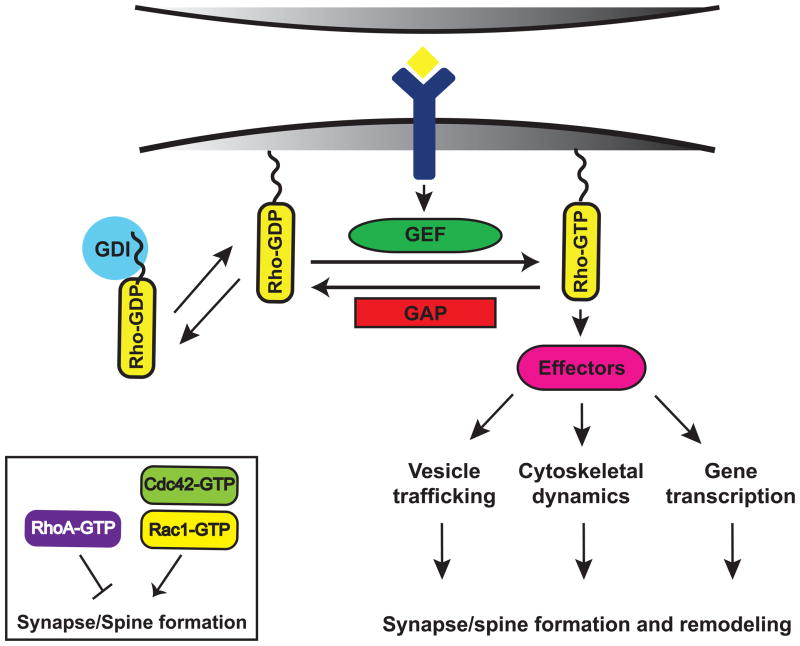
Figure 2. Model of Rho GTPase signaling at synapses.
Rho GTPases function as binary switches by cycling between an active, GTP-bound form and an inactive, GDP-bound form. Rho GTPase activity is tightly regulated in space and time by three different classes of regulatory proteins: guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), GTP-activating proteins (GAPs), and guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (GDIs). In their active state, Rho GTPases interact with downstream effectors that regulate a variety of cellular processes, which ultimately contribute to spine morphogenesis and excitatory synapse development. The Rho GTPases Rac and Cdc42 promote the formation and growth of synapses and spines, whereas RhoA inhibits synapse development.