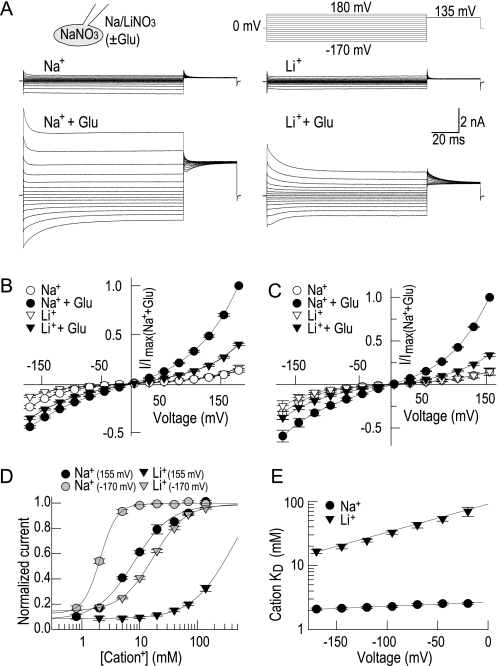
FIGURE 1.
Li+ substitutes for sodium in activating EAAT4 anion currents. A, representative current recordings from cells expressing EAAT4 in sodium and lithium-based bath solutions in the absence or presence of saturating concentrations of l-glutamate. B and C, current-voltage relationship of steady-state current amplitudes (n = 4) under standard NaNO3-based (B) or KNO3-based (C) internal solutions. D, concentration-response curves of steady-state currents with external sodium or lithium in the presence of 20 mm l-glutamate. After normalization, data were fitted with Hill equations with the following apparent KD values for sodium: 2.1 ± 0.1 mm (−170 mV) and 8.6 ± 0.5 mm (+155 mV) with Hill coefficients ranging from 2.7 ± 0.2 (−170 mV) to 1.3 ± 0.1 (+155 mV); and for lithium, the apparent KD values were as follows: 16.6 ± 1.2 (−170 mV) and >100 mm (+155 mV) and Hill coefficients of 1.5 ± 0.1 (−170 mV) (n = 4–7). E, voltage dependence of apparent cation affinities shown on the semi-log scale. Log(KD) fitted with linear functions with slopes of 0.65 ± 0.05·10−3/mV for sodium and 4.40 ± 0.32·10−3/mV for lithium binding (n = 4–7).