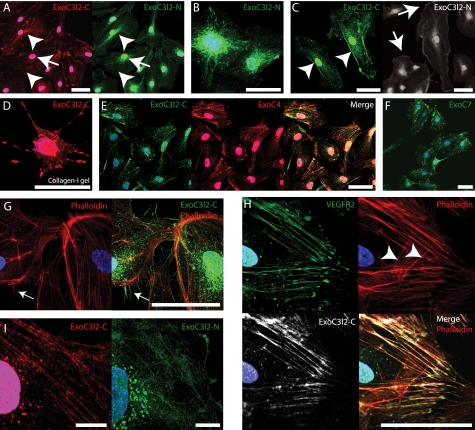
FIGURE 4.
The EXOC3L2 protein partially co-localizes with EXOC4 and VEGFR2. A–C, HMVECs grown on a two-dimensional surface and stained with antibodies directed against the central part (ExoC3l2-C) or the N-terminal part (ExoC3l2-N) of the EXOC3L2 protein sequence. Both antibodies stain nuclei, perinuclear vesicles (A, arrowheads), and stress fibers (A, arrows), but have a slightly different appearance in the peripheral regions. ExoC3l2-C stains the lateral part of the cell membrane (C, arrowheads), whereas anti-ExoC3l2-N stains the more dynamic, expanding or retracting, regions (C, arrows). D, HMVEC grown in collagen I gel stained for ExoC3l2-C. E and F, ExoC3l2-C co-localizes to a large extent with EXOC4 (Overlap coefficient = 0.75 ± 0.07) (E), which is also found predominantly associated with stress fibers and vesicles, whereas EXOC7 (F) shows a different staining pattern. G, filopodia stained with ExoC3l2-N (arrow). Actin fibers are visualized with phalloidin. H, ExoC3l2-C and VEGFR2 antibodies stain longitudinal actin fibers but not latitudinal (arrowheads) (overlap coefficient = 0.73 ± 0.04). Scale bars = 50 μm. I, ExoC3l2-C and ExoC3l2-N staining in ×63 magnification. Scale bars = 10 μm.