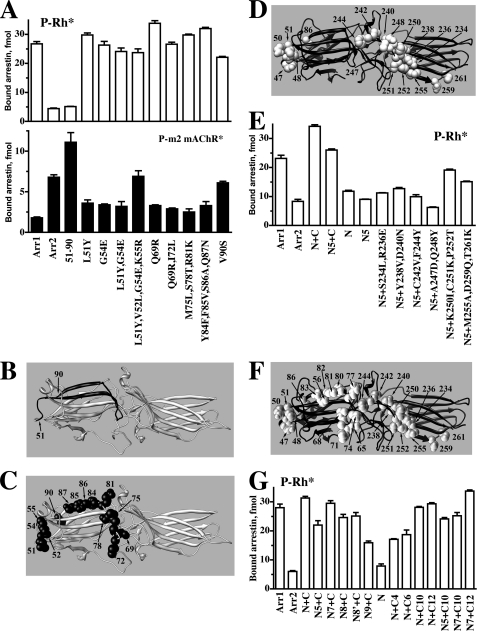
FIGURE 3.
Identification of arrestin residues that determine receptor specificity. A–C, shown is the binding to P-Rh* (upper panel) and phosphorylated M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (P-m2 mAChR*) of arrestin-1 (Arr1), arrestin-2 (Arr2), arrestin-1 with the N-domain residues 51–90 replaced with arrestin-2 residues 47–86 (51–90) (shown in panel B; arrestin-1- and arrestin-2-derived elements and residues are shown in gray and black, respectively), and arrestin-1 mutants with the indicated residues replaced with the corresponding arrestin-2 residues (shown as black CPK models on gray arrestin-1 molecule in panel C). D, arrestin-2 molecule (black) with arrestin-1 residues introduced in the mutants characterized in panel E are shown as gray CPK models. E, direct binding to P-Rh* of Arr1, Arr2, and Arr2 with elements 47–86 and 233–261 replaced with arrestin-1 elements 51–90 and 239–267, respectively (N+C), Arr2 replaced with a quintuple mutation (Y47L,L48V,E50G,R51K,S86V) in the N-domain, residues 233–261 replaced with the arrestin-1 element 239–267 (N5+C), element 47–86 replaced with arrestin-1 residues 51–90 (N), and with combinations of N5 quintuple mutations in the N-domain and the indicated mutations in the C-domain element. F, arrestin-2 molecule (black) with all arrestin-1 residues introduced in the mutants characterized in panel G are shown as gray CPK models. G, direct binding to P-Rh* of arrestin-2 with the indicated elements replaced with the corresponding residues from arrestin-1: N7, N5+R65Q+L68I; N8, N5+L71M+T74S+K77R; N8, N7+T56S; N9, N5+F80Y+V81F+A82S+N83Q; C4, S234L+R236E+Y238V+D240N; C6, K250I+C251K+P252T+M255A+D259Q+T261K; C10, C4+C6; C12, C10+C242V+F244Y. Binding experiments were performed 2–3 times in duplicate. Means ± S.D. are presented.