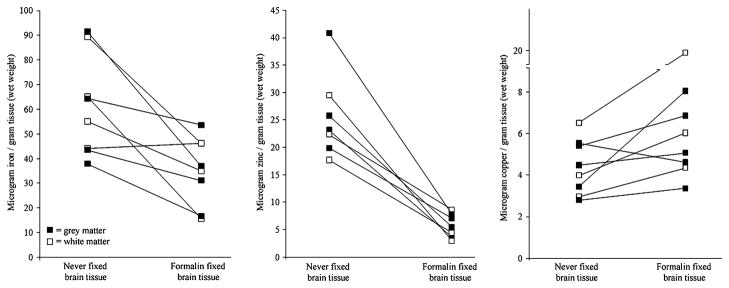
Fig. 1.
Effect of long-term formalin archival on transition metal levels in paired Alzheimer’s disease brain samples Iron levels were found to decrease by about 40% upon fixation in formalin (P<0.01), zinc levels were shown to decrease with fixation by about 75% (P <0.0001) and copper increased by about 40% (P <0.05). All of these effects appeared to be independent of whether the tissue was collected from grey matter or white matter. Lines between specimens indicate they were taken from the same brain