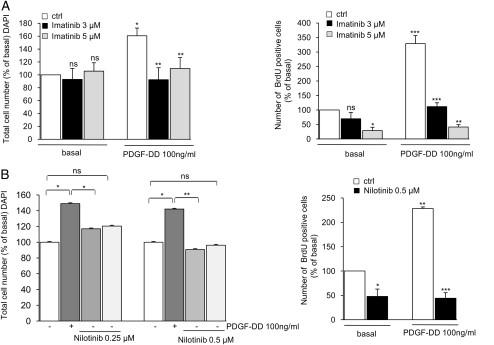
Fig. 2.
Basal and PDGF-DD–mediated proliferation of schwannoma cells during treatment with imatinib and nilotinib. (A and B) Imatinib and nilotinib significantly inhibited basal and PDGF-DD–mediated proliferation of schwannoma cells. Nilotinib displayed higher efficiency than imatinib, partly inhibiting PDGF-DD–mediated proliferation at a concentration of 0.25 µM (B; left panel) and reaching a maximal effect in the inhibition of both basal and PDGF-DD–mediated proliferation at a concentration of 0.5 µM (B; left and right panels). The maximum effects of imatinib were reached at 3 µM for the inhibition of PDGF-DD–mediated proliferation and 5 µM for basal proliferation. Cells were cultured in serum-free medium for 72 hours in the presence or absence of imatinib, nilotinib, and 100 ng/mL PDGF-DD. The inhibitors were added 40 minutes before stimulation with PDGF-DD. Cell proliferation was monitored by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole staining and BrdUrd incorporation. The data are normalized to basal (nonstimulated) levels and given as % of basal (100%). Data are mean±SEM.