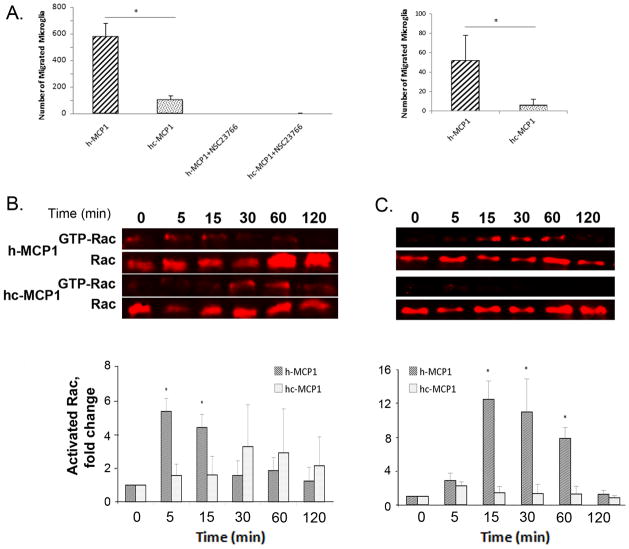
Figure 2. Mouse MCP1 C-terminal extension decreases the chemotactic potency of human MCP1 and the chemotactic activity depends on Rac1.
A. Primary mouse microglia (left) or the CHME3 human microglial line (right) were plated and evaluated for chemotaxis in response to recombinant hMCP1 or hc-MCP1, in the presence or absence of the Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766. Each experimental condition was assayed in triplicate. Data are expressed as Mean ± SD. **, p<0.01. B. N9 microglial cells or C. CHME3 human microglial cells were treated with 10nM MCP1 over time. The activated Rac1 was immunoprecipitated using GST-PBD beads. At each time point, the activated and total Rac1 were detected by western blotting. Western blots of activated and total Rac1 and quantification of the blots for hMCP1 and hc-MCP1. The blots were normalized to the 0 time point. Each experimental condition was assayed in triplicate and the data were expressed as Mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, compared to 0 time point.