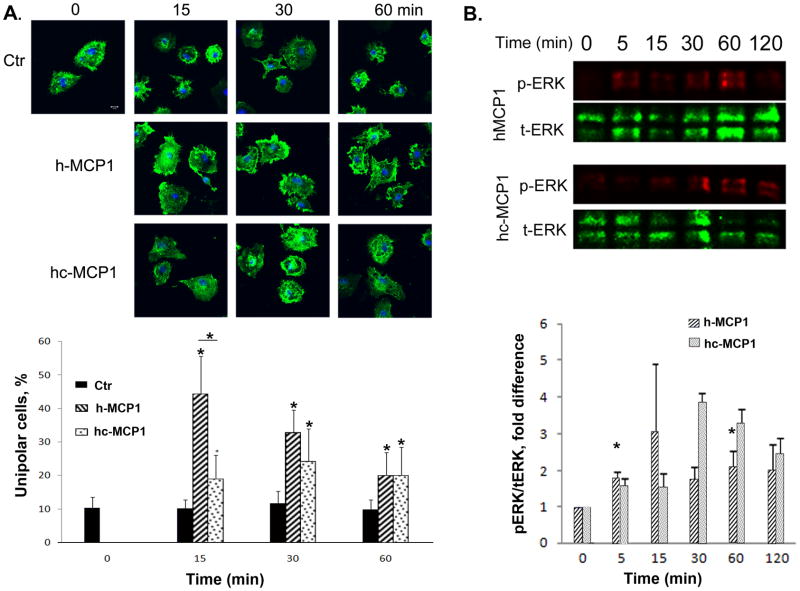
Figure 3. Mouse MCP1 C-terminus inhibits the formation of lamellipodia induced by human MCP1.
A. Primary microglia plated on coverslips were incubated with a point source of recombinant MCP1 proteins for different periods of time. At each time point, the cells were washed, fixed, and stained for actin cytoskeleton using Alexa-Phalloidin. Scare bar = 10 μm. The percentage of unipolar cells (migrating towards the focal point of MCP1 protein) was quantified. Data are expressed as Mean ± SD. N=9. *p<0.05. B. Mouse MCP1 C-terminus changes the activation pattern of ERK on microglia. Primary microglial cells were treated with h-or hc-MCP1 over time. At each time point, cell lysates were collected and analyzed for phosphorylated and total ERK1/2 by western blotting. Experiments were performed in triplicate. Representative experiment shown. Data are expressed as Mean ± SD. *p<0.05, compared to 0 time point.