Fig. 2.
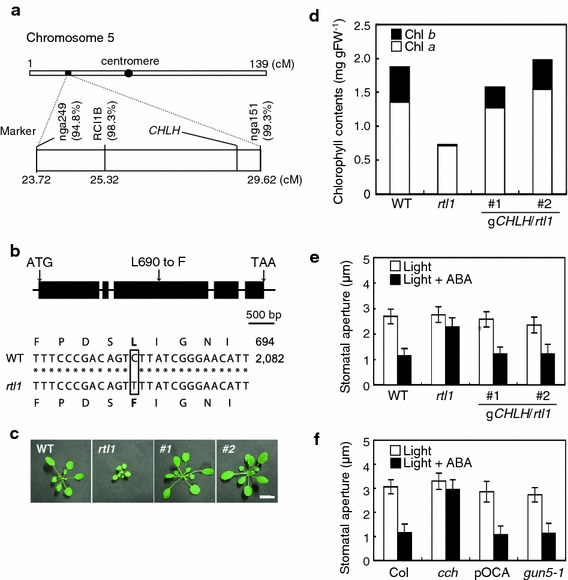
CHLH missense mutation is responsible for the rtl1 phenotype. a Mapping analysis of the RTL1 locus. The RTL1 locus was close to SSLP marker nga151 and Mg-chelatase H subunit (CHLH). b Schematic representation of the structure of the CHLH gene (upper). Black boxes and lines represent exons and introns, respectively. The position of the amino acid substitution (L690 to F) in rtl1 is indicated. The partial sequences of CHLH cDNA and the deduced amino acid in wild-type (WT) and rtl1 are shown (lower). A single nucleotide substitution (C2068 to T) is shown by a box. The amino acid and nucleotide numbers are indicated on the right. c Typical phenotypes in the WT, rtl1, and two independent gCHLH/rtl1 complementation lines (#1 and #2). Plants were grown on soil for 4 weeks. Bar 10 mm. d Chlorophyll contents in rosette leaves of 4-week-old WT, rtl1, and gCHLH/rtl1 lines (#1 and #2). The bars show the contents of chl a (white) and chl b (black). e ABA-induced stomatal closing in WT, rtl1, and gCHLH/rtl1 lines (#1 and #2). Conditions were the same as shown in Fig. 1d. Data represent the mean with SD. f ABA-induced stomatal closing in the known chlh mutants, cch and gun5. Col and pOCA are the background plants of the cch and gun5-1 mutation, respectively. Conditions were the same as shown in Fig. 1d. Data represent the mean with SD. All experiments were repeated three times on different occasions with similar results
