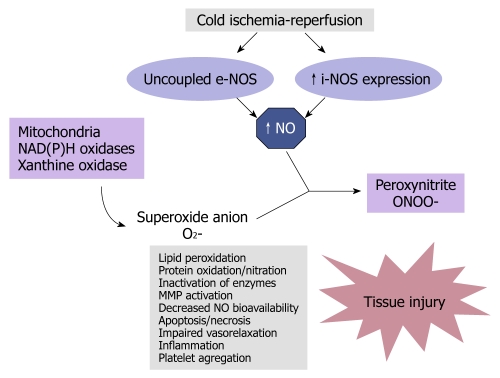
Figure 3.
Tissue damage after unbalanced nitric oxide production. Cold ischemia reperfusion involves uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase (e-NOS) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (i-NOS) expression. Large amounts of nitric oxide (NO) are produced under these pathological conditions. NO, in association with increased mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, reacts with superoxide anion (O2-), to produce peroxynitrite (ONOO-). Peroxynitrite, in concert with other oxidants, induces tissue damage.