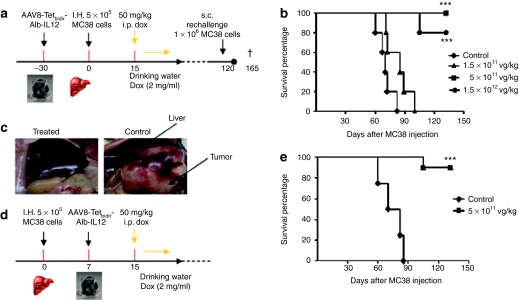
Figure 4.
Intravenous administration of AAV8-Tetbidir-Alb-IL-12 results in antitumoral activity. (a) Schematic representation of the antitumoral prophylactic study. (b) C57BL/6 female mice were injected with three different doses of AAV8-Tetbidir-Alb-IL-12 vector 1.5 × 1012, 5 × 1011, 1.5 × 1011 vg/kg (n = 10). A group of mice were inoculated with saline solution instead of vector and doxycycline (Dox) (control group) (n = 10). One month after vector administration, hepatic tumors were established by direct implantation of 5 × 105 MC38Luc1 cells in the left liver lobe following medial laparotomy of isofluorane-anaesthetized mice. Cell engraftment was verified by bioluminescence 2–3 days later. Ten days after the inoculation of the tumor cell, interleukin (IL)-12 expression induction was performed as described previously, that is, by intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of 50 mg/kg, followed by administration of Dox via drinking waster for 6 days. (c) Representative images from a mouse belonging to the group treated with 5 × 1011 vg/kg AAV8-Tetbidir-Alb-IL-12 and a mouse treated with saline. (d) Schematic representation of the antitumoral therapeutic study. (e) Hepatic tumors were established by direct implantation of 5 × 105 MC38Luc1 cells in the left liver lobe following medial laparotomy of isofluorane-anaesthetized mice. Cell engraftment was verified by bioluminescence 2–3 days later. Seven days after tumor injection mice were treated with vg/kg of AAV8-Tetbidir-Alb-IL-12 vector or saline (n = 10). Fifteen days after the inoculation of the tumor cell, IL-12 expression induction was performed as described previously, that is, by i.p. administration of 50 mg/kg, followed by administration of Dox via drinking waster for 6 days. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of mice with established MC38 tumors after treatment is assessed (***P < 0.01). AAV8, adeno-associated virus serotype 8; Alb, albumin promoter; s.c. subcutaneous.