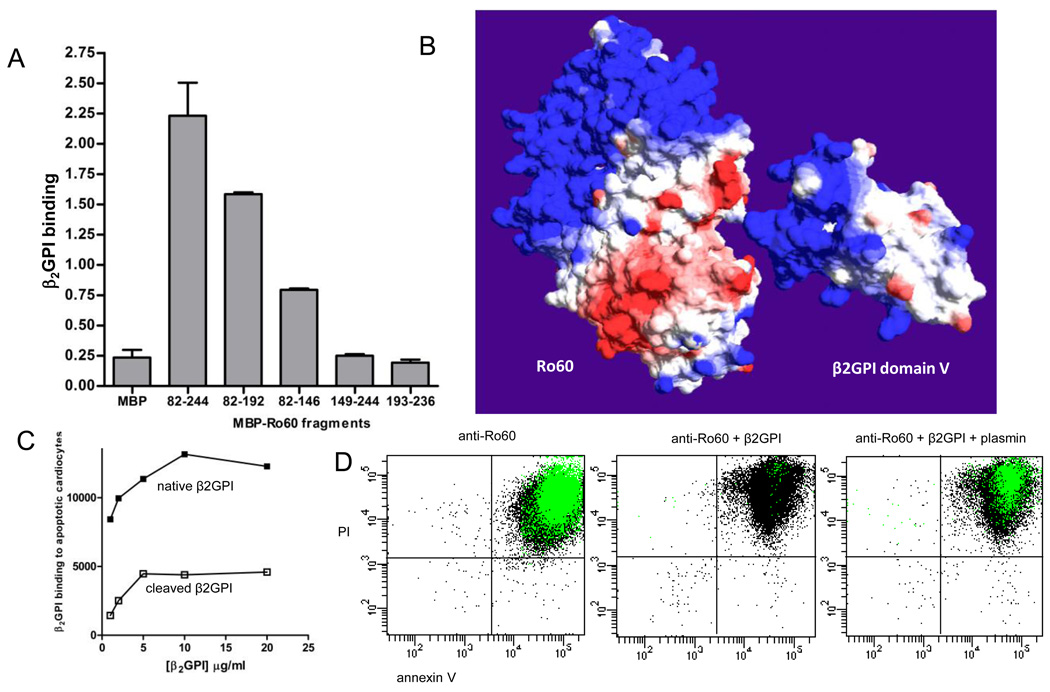
FIGURE 3.
The Ro60 binding site on β2GPI is within the plasmin cleavage site, Lys317-Thr318. (A) The β2GPI binding site on Ro60 was measured by ELISA using recombinant maltose binding protein (MBP) expressing various regions of Ro60. Ro60 fragments encompassing amino acids (aa) 82–244, aa 82–192, and aa 82–146 bound to purified native human β2GPI compared to MBP-Ro60 aa 149–244, aa 193–236, and MBP control. Values are the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of triplicate determinations (n=3). (B) Molecular surface models of Ro60 and β2GPI with the β2GPI fifth domain oriented towards a cleft in Ro60 formed by the mapped aa 82–146 region. Surface colours are calculated using a coulombic algorithm for electrostatic potential where blue is positive charge, white is neutral, and red is negatively charged. (C) The binding of β2GPI to apoptotic cardiomyocytes is abrogated by plasmin cleavage. (D) Plasmin reverses the β2GPI-mediated inhibition of anti-Ro60 binding to apoptotic cells. Representative flow cytometry dot plots depicting the binding of anti-Ro60 IgG (green) to late apoptotic cells (n=5).