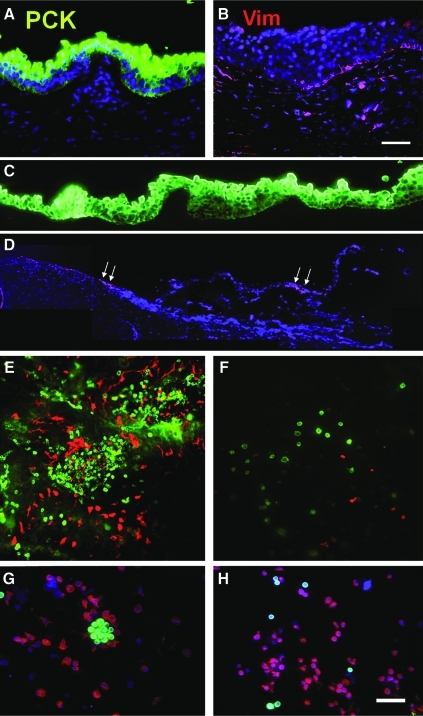
FIG. 1.
Double immunofluorescence staining of pan-cytokeratins (PCK, green) and Vimentin (Vim, red). PCK+ full-thickness epithelium was present in the cryosectioned human limbal tissue (A), whereas scattered Vim+ cells were subjacent to the epithelium (B). Dispase digestion at 4°C/16 h removed the entire PCK+ epithelial sheet (C). There were no PCK+ cells in the cross section of the remaining stroma, whereas some Vim+ cells were present in the basement membrane area (marked by white arrows) and the stroma (D). Wholemount preparation of the remaining limbal stroma showed in the en face optical image aggregations of numerous PCK+ and Vim+ cells at limbus region (E), but few scattered PCK+ and Vim+ cells in the peripheral cornea (F). Cytospin preparation of cells released from the remaining stroma by collagenase digestion revealed many PCK+ clusters (G) that were associated with Vim+ cells. When these cells were further treated with T/E, PCK+ clusters disappeared and single PCK+ cells were intermixed with Vim+ cells (H). Nuclear counterstaining was performed using Hoechst 33342. Scale bar = 100 μm. T/E, trypsin/EDTA. Color images available online at www.liebertonline.com/tec