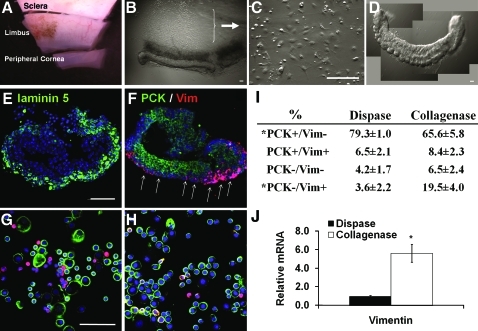
FIG. 2.
Limbal clusters obtained by collagenase digestion. A corneoscleral rim was subdivided into 12 segments, among which each was further trimmed off 1 mm above and below the limbal region (A). Each limbal segment was subjected to collagenase digestion in SHEM at 37°C for 18 h to yield a compact pigmented limbal cluster (B). After additional 24 h culturing on plastic in SHEM, the remaining cells adhered on plastic (C). Each cluster could be manually transferred by a pipette (D). Tangential sectioning of a cluster showed the preservation of laminin 5 (green) on the basal layers (E). Double immunostaining revealed that the cluster contained PCK+ cells (green) and Vim+ (red) cells, which were preferentially distributed on the basement membrane side (F, white arrows). Double immunostaining of cytospin preparations derived from collagenase-isolated clusters revealed more Vim+ cells (G, n = 1200) than those derived from dispase-isolated sheets, which had more PCK+ cells (H, n = 834). Such a difference was confirmed by counting of PCK+ cells and Vim+ cells using Zeiss image analysis (I, from 3 different bright fields and each derived from 3 donors, *p < 0.05). qRT-PCR confirmed a significant sixfold high expression of Vim mRNA in collagenase-isolated clusters than dispase-isolated sheets (J, *p < 0.05, triplicate from 3 donors). Scale bars = 100 μm. SHEM, supplemented hormonal epithelial medium; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Color images available online at www.liebertonline.com/tec