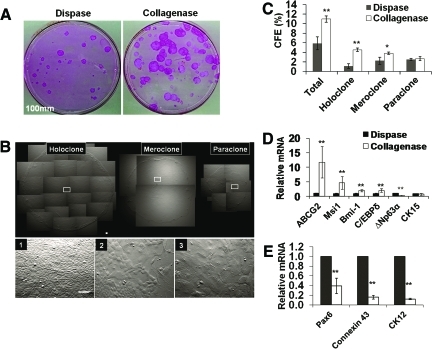
FIG. 3.
Comparison of clonal growth between dispase-isolated sheets and collagenase-isolated clusters. Significantly more rhodamine B-stained clones were generated by collagenase-isolated clusters than dispase-isolated sheets when 500 single cells were seeded in a 100-mm dish containing mitomycin C-treated 3T3 fibroblast feeder layers and cultured in SHEM for 9 days (A). Three different types of clones, that is, holoclone, meroclone, and paraclone, were identified based on the smoothness of the border and the cell size in the center of the clone with uniformly small cells, mixture of small and large cells, and uniformly large cells, respectively (see 1, 2, and 3 derived from respective insets) (B). Collagenase-isolated clusters had a significantly higher percentage of holoclones and meroclone (C, n = 3, *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.001). qRT-PCR revealed that collagenase-isolated clusters had a significant higher expression of ABCG2, Msi-1, Bmi-1, and C/EBPδ transcripts (D), but a lower transcript expression of ΔNp63α, cytokeratin 12 (CK12), connexin 43, and Pax6 (E) when compared to dispase-isolated sheets (n = 3, **p < 0.001). No significant difference was found in transcript expression of CK15 (D). Scale bar = 100 μm. Color images available online at www.liebertonline.com/tec