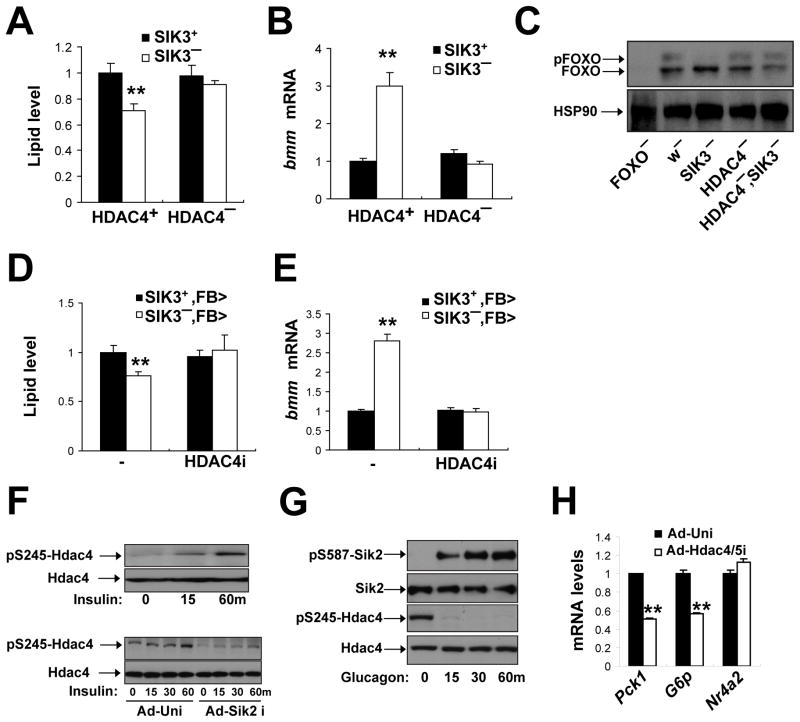
Figure 7. SIK3 inhibits FOXO activity via an HDAC4-dependent mechanism.
(A–C) Effect of HDAC4 gene disruption on lipid levels (A) bmm mRNA amounts (B), and FOXO phosphorylation (C) in SIK3 mutant relative to control flies. Data panels A and B is from ad libitum fed flies. Data in panel C was from 1 hour refed flies. Genotypes are: SIK3+(w), SIK3− (SIK348), SIK3+, HDAC4− (HDAC4KG09091/HDAC4e04575), and SIK3−, HDAC4− (HDAC4KG09091/HDAC4e04575; SIK348), FOXO− (FOXO21/FOXO25). (n=24 per genotype).
(D, E) Effect of fat body-specific depletion of HDAC4 (HDAC4i) on lipid levels (D) and bmm mRNA amounts (E) in SIK3 mutant relative to control flies under feeding conditions. Genotypes are: SIK3+,FB>(FB-GAL4/+), SIK3−,FB> (FB-GAL4,SIK348/SIK348), SIK3+,FB>HDAC4i(FB-GAL4/+;UAS-HDAC4 RNAi/+), and SIK3−, FB>HDAC4i (FB-GAL4,SIK348/SIK348; UAS-HDAC4 RNAi/+). (n=14–16 per genotype).
(F) Immunoblot showing amounts of phosphorylated mouse HDAC4 in extracts from primary hepatocytes following RNAi-mediated depletion of SIK2. Effect of exposure to insulin (100nM) for different times (in minutes) indicated.
(G) Immunoblot showing effect of glucagon (100nM) on HDAC4 phosphorylation at Ser245 and on inhibitory phosphorylation of SIK2 at Ser587 in primary mouse hepatocytes.
(H) Q-PCR analysis of PEPCK, Glucose 6 phosphatase, and NR4A2 mRNA amounts in primary hepatocytes following exposure to glucagon (100nM) for 1 hour. Effect of adenovirus encoded HDAC4/5 RNAis shown.