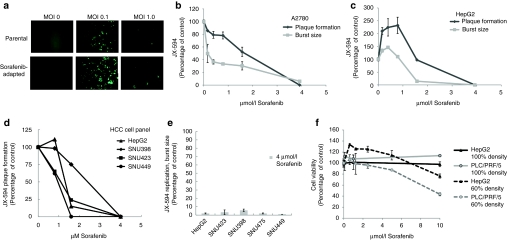
Figure 1.
JX-594 replication in liver cancer lines is inhibited in the presence of sorafenib in vitro. (a) Infectability of PLC/PRF/5 (human hepatoma) cells (parental) and sorafenib-adapted PLC/PRF/5 cells was determined by addition of JX-594 expressing green fluorescent protein at multiplicities of infection (MOI) of 0, 0.1 and 1. Images were taken with a Zeiss Axiovision microscope fluorescent microscope and analyzed using Axiovision acquisition and image storage software 24 hours postinfection. (b,c) JX-594 replication in the presence of sorafenib was measured by plaque formation and burst assay after incubation with sorafenib for 3 days (plaque formation assay) or 24 hours (burst assay). Results are expressed as percent of no-sorafenib control (replicate mean + SD). (d) The ability of JX-594 to form plaques in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of sorafenib on monolayers of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines. Results are expressed as percent of no sorafenib control. (e) JX-594 replication was tested by burst assay using a panel of HCC cell lines infected at MOI of 0.1 for 2 hours, followed by change to media with 4 µmol/l sorafenib. After 48 hours, cells and supernatants were collected for titration by plaque assay on A2780 cells. Results are expressed as percent of no-sorafenib control (replicate mean + SD). (f) Cell viability in the presence of sorafenib was determined 24 hours after addition of sorafenib to PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2 cells plated at 60% and 100% densities. Results are expressed as percent of no-sorafenib control (replicate mean + SD).