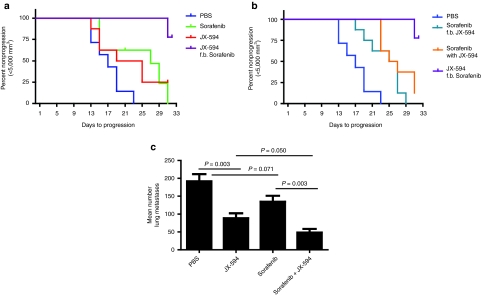
Figure 2.
Combination therapy with sorafenib enhances JX-594 efficacy in two murine tumor models. (a,b) SCID mice with subcutaneous HepG2 tumors of 12–14 mm diameter were randomized to five groups and treated with PBS, daily sorafenib, weekly JX 594, simultaneous sorafenib and JX-594, or sequentially treated with sorafenib for 2 weeks followed by JX-594, or with 2 weekly dose of JX-594 followed by sorafenib. Analysis of time-to-tumor-progression (TTP) was performed. Kaplan–Meier curves show TTP, with 5,000 mm3 tumor volume considered as progression. (c) B16 model of lung metastases: C57BL/6 mice were injected with 3 × 105 B16-F10-LacZ cells intravenously and 24 hours later were treated with phosphate buffered saline (PBS), sorafenib alone (50 µg/kg per oral dosing daily for 2 weeks) JX594 alone (107 plaque-forming units (pfu) intravenously three times per week for 1 week) or in combination (n = 5 per group). Three weeks after treatment initiation, mice were killed and lungs were fixed and stained to detect surface B16 tumor nodules.