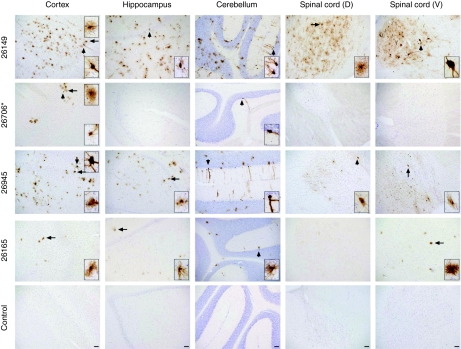
Figure 7.
Intravascular injection of adeno-associated virus serotype 9 (AAV9) in nonhuman primates (NHPs) results in broad central nervous system central nervous system (CNS) transduction that is limited by an anti-AAV9 immune response. NHPs were injected with scAAV9/CBh-GFP via the carotid artery (i.c., animals 26149 and 26706) or the saphenous vein (intravenous, animals 26945 and 26165). Green fluorescent protein (GFP) biodistribution was assessed by immunohistochemistry 4 weeks after injection. Examples of GFP expression detected by 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrachloride staining in the cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum, dorsal (D) and ventral (V) spinal cord are shown for each animal. Arrows point to GFP-positive cells highlighted in the magnified insets with neuronal (short arrow) or glial (long arrow) morphology. An asterisk (*) denotes that NHP 26706 had detectable pre-existing neutralizing antibodies (see Table 1). Bar = 100 µm.