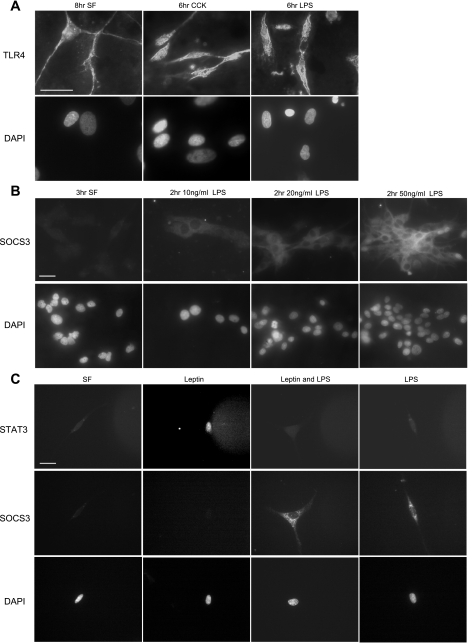
Fig. 6.
Exposure of vagal afferent neurons to LPS increases expression of SOCS-3 and inhibits leptin-induced phosphorylation of STAT3. A: photomicrographs of nodose neurons in culture immunostained for Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR-4). TLR-4 immunoreactivity was localized to both the plasma membrane and the membrane of neurons; exposure to either CCK or LPS had no observable effect on either levels of expression or cellular localization. B: photomicrographs of SOCS-3 (top) and nuclear staining (bottom) from cultured vagal afferent neurons in response to increasing doses of LPS (0–50 ng/ml). SOCS-3 is dose-dependently upregulated in response to LPS; n = 6. C: photomicrographs of phosphorylated STAT3 (top) and nuclear staining (bottom) from cultured vagal afferent neurons under serum-free conditions in response to leptin alone, LPS alone, or leptin and LPS together. LPS alone had no effect on pSTAT3 but increased expression of SOCS-3. LPS inhibited leptin-induced STAT3 phosphorylation; n = 8. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.