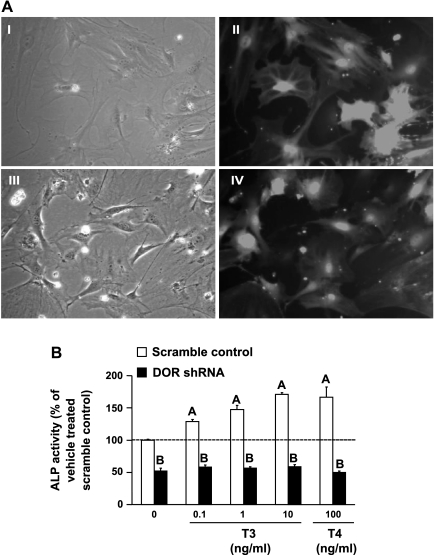
Fig. 4.
TH-induced increase in ALP activity is severely reduced in primary calvaria osteoblasts transduced with DOR shRNA. A: transduction efficiency of primary calvaria osteoblasts transduced with scramble control or DOR shRNA. Pictures are representative of scramble control-bright field (I), scramble control-GFP fluorescence (II), DOR shRNA-bright field (III), and DOR shRNA-GFP fluorescence (IV). Images were taken at ×40 magnification with an Olympus IX70. B: scramble control and DOR shRNA primary calvaria osteoblasts were treated with T3 (0.1, 1, and 10 ng/ml) or T4 (100 ng/ml), and ALP activity was determined 72 h after treatment. Values are presented as %vehicle-treated scramble control ± SE (n = 6). Basal ALP activity values of scramble control (43.1 mU/mg protein ± 0.67) and DOR shRNA (21.2 mU/mg protein ± 1.5). Data were analyzed by 2-way ANOVA, and a significant interaction was observed between gene and treatment. AP < 0.05 vs. vehicle treated control; BP < 0.001 vs. scramble control at corresponding dose.