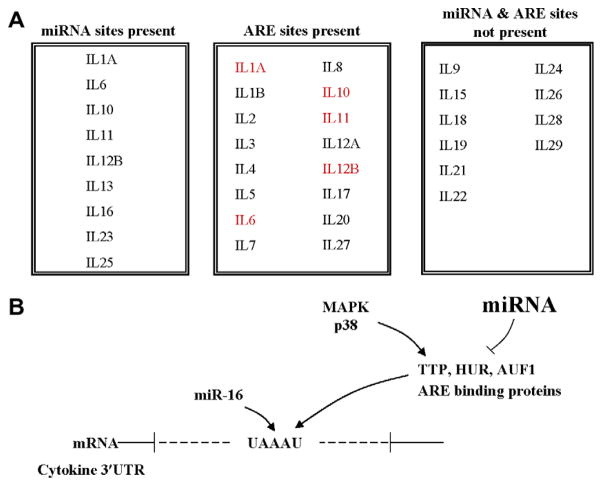
Fig. 3.
Cytokines may be regulated both directly and indirectly by miRNA. (A) Post-transcriptional regulation of the interleukin genes mediated via miRNA and ARE sites in the 3′UTR. Interleukin genes with predicted miRNA binding sites are indicated in the first box. Those with ARE sites [20] are listed in the second box where the text in red signifies predicted regulation by both miRNAs and AREs. (B) Indirect miRNA regulation of genes (e.g., cytokine genes) having AU-rich sites in their 3′UTR. miRNA potentially regulate the expression of the components of the ARE machinery. Additionally, MAPKs regulate the function of ARE-BPs and they may in turn be regulated by miRNA [5]. MiR-16 sites are found to overlap with some ARE sites and could potentially provide another mechanism by which miRNA regulate the expression of ARE-containing transcripts like SOCS3 (see Section 9).