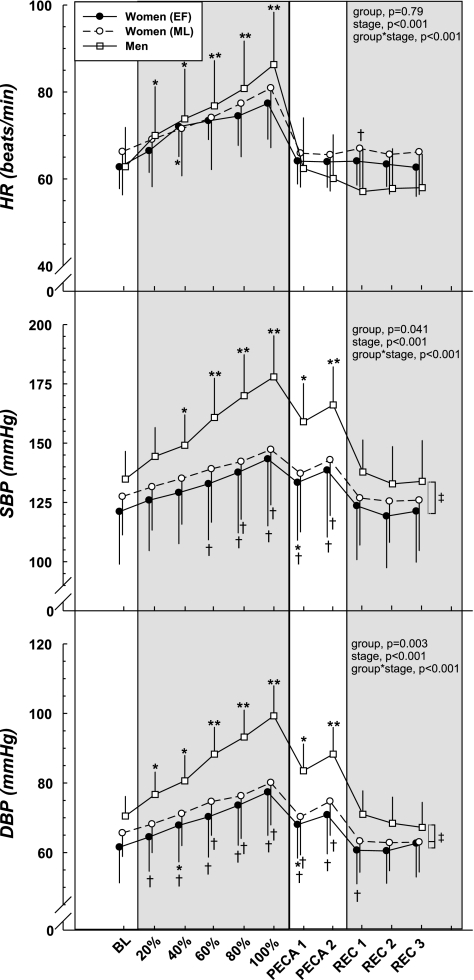
Fig. 2.
Cardiovascular responses during static handgrip exercise and postexercise circulatory arrest (PECA). Static handgrip elicited increases in heart rate (HR), systolic blood pressure (SBP), and diastolic BP (DBP) where men demonstrated higher BP than the women. Similarly, PECA induced higher BP compared with baseline (BL) in both sexes with the women showing an attenuated response compared with the men. Low vs. high hormone status did not affect the responses to either static handgrip or PECA in women. REC, recovery. *Group difference compared with BL, P < 0.05. **Difference from BL (all groups), P < 0.05. †Sex difference within stage, P < 0.05. ‡Group difference (main effect), P < 0.05.