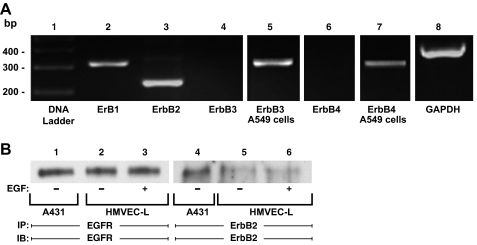
Fig. 4.
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and ErbB2 expression in HMVEC-Ls. A: RNA was isolated from postconfluent HMVEC-Ls. Complementary DNA was generated from RNA using oligo (dT) primers and reverse transcriptase. This cDNA was used as a template for amplification with DNA polymerase and primers corresponding to EGFR or ErbB1 (lane 2), ErbB2 (lane 3), ErbB3 (lanes 4-5), and ErbB4 (lanes 6-7), as well as GAPDH as a housekeeping gene control (lane 8). The control DNA ladder is shown on the left (lane 1). A549 cells served as the positive controls for both ErbB3 (lane 5) and ErbB4 (lane 7). The DNA ladder, ErbB1, ErbB2, ErbB3, ErbB4 and GAPDH (lanes 1-4, 6, and 8) were run on the same gel, whereas the ErbB3 and ErbB4 positive controls (lanes 5 and 7) were run on separate gels. B: total cell lysates from EGF-exposed (lanes 3 and 6) and control (lanes 2 and 5) HMVEC-Ls were immunoprecipitated with either anti-EGFR or anti-ErbB2 antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF, and each blot was probed with the immunoprecipitating antibody. The total cell lysates from A431 epithelial cells served as the positive controls for both EGFR and ErbB2 proteins (lanes 1 and 4).