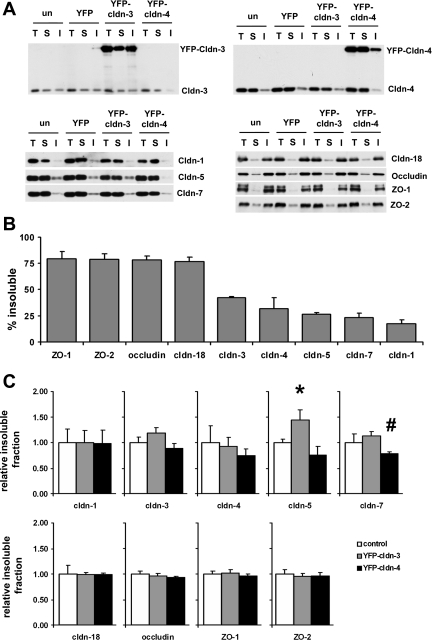
Fig. 8.
Alveolar epithelial tight junction proteins exhibit a range of Triton X-100 insolubility. A: primary rat alveolar epithelial cells were untreated or transduced on day 4 with YFP-Cldn-3, YFP-Cldn-4, or YFP alone, further incubated for 2 days, and then analyzed by Triton X-100 extraction to quantify the insoluble pool of Cldn-1, Cldn-3, Cldn-4, Cldn-5, Cldn-7, Cldn-18, occludin, ZO-1, and ZO-2. T, total protein samples; S, Triton X-100-soluble fractions; I, Triton X-100-insoluble fractions. B: by densitometric analysis, alveolar epithelial tight junction proteins isolated from untreated cells showed a range of insolubility from 75% to 15%. Values are means ± SE (n = 3–4). C: cells expressing YFP-Cldn-3 showed significantly more Cldn-5 associated with the Triton X-100-insoluble pool than controls or cells expressing YFP-Cldn-4 (*P < 0.05). Cells expressing YFP-Cldn-4 exhibited decreased Cldn-7 insolubility compared with cells expressing YFP-Cldn-3 (#P < 0.05).