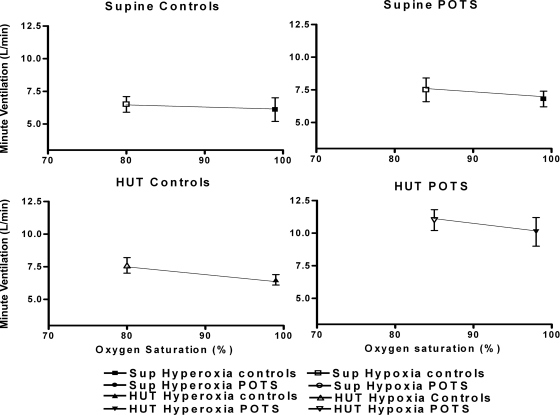
Fig. 2.
Hypoxic ventilatory response/peripheral chemoreceptor sensitivity (in l·min−1·%oxygen−1) averaged over all control subjects (left) and averaged over all postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS) patients (right). Top: results in supine (Sup) the position. Bottom: results during head-up tilt (HUT) position. These data depict the minute ventilation response to decrease in O2 saturation during peripheral chemoreceptor stimulation. Supine ventilation is increased in POTS compared with control subjects (P < 0.05). Baroreflex unloading by HUT further increases minute ventilation in POTS patients and translates the set point upward and toward the right.