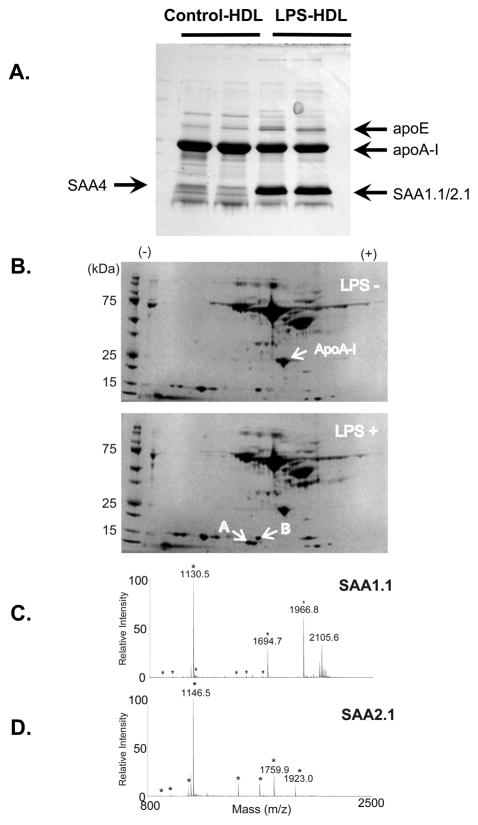
Figure 2. MALDI-TOF analysis.
HDL (d=1.063–1.210 g/mL) was isolated by ultracentrifugation from plasma of control and LPS-injected mice. HDL (20 μg protein) was separated by SDS-PAGE (10 – 20 % gradient gel) and the gel was stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Each gel band corresponding to the apparent molecular weight of SAA1.1/2.1, SAA4, apoA-I and apoE was cut out, digested with trypsin, and the peptide digest was extracted for tandem mass spectrometric analysis by MALDI-TOF. The arrows indicate bands that were identified by MALDI-TOF and database searching that contained peptides unique to SAA1.1/2.1, SAA4, apoA-I, and apoE (Figure 2A).
Albumin-depleted plasma samples (20 μl) from control (A) and LPS-injected (B) mice were separated by two dimensional electrophoresis (first dimension: IEF pH 3–10, second dimension: 10% SDS-PAGE) and the gel was stained with a silver stain. Selected spots from 2D gels were identified by in-gel tryptic digest and MALDI-TOF analysis. The small arrows indicate bands that were identified by tandem MS/MS MALDI-TOF and database searching that contained peptides unique to SAA1.1, SAA2.1, and apoA-I (Figure 2B). The spot designated as SAA2.1 was identified as such with a MASCOT MOWSE score of 374 (CI 100% - Figure 2C), and the adjacent spot was identified as SAA1.1 with a MOWSE score of 403 (CI 100% - Figure 2D). The asterisks indicate peaks corresponding to SAA peptides.