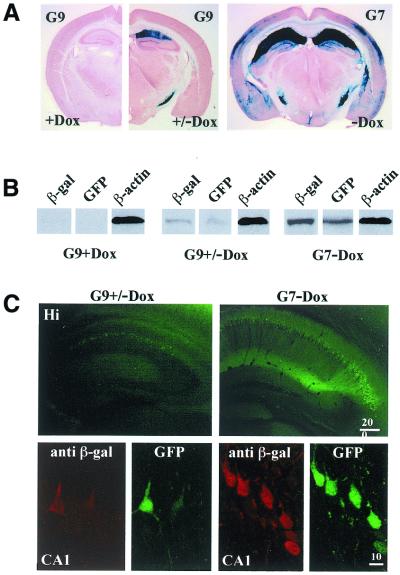
Figure 4.
Dox-regulated tTA activity, monitored in responder line G9. (A) Coronal brain sections of TgCaMK2tTA/GFPtetO7lacZ mice derived from line G9 and G7 at P42, stained for β-galactosidase activity. Activation by tTA is compared between animals raised under Dox (G9+Dox) to littermates for which Dox was removed at P21 (G9+/–Dox) and to mice of line G7 (G7–Dox). Without Dox, high expressing mice of line G9 die at ∼3 weeks of age and cannot be used as controls. (B) Immunoblot analysis of whole mouse brain extracts, which were obtained from mice raised under identical experimental conditions as in (A). Each lane represents three separate experiments and antibodies used for the detection are indicated in the top of each panel. β-Actin served as internal standard. (C) GFP and β-galactosidase expression in hippocampi (Hi) of tTA-induced G9 (G9+/–Dox) and untreated G7 mice (G7–Dox) at P42. Confocal analysis (lower part) was performed in CA1 pyramidal cell layers. Dox treatment and removal (G9+/–Dox) leads to GFP and β-galactosidase induction in few CA1 pyramidal neurons. An increased number of CA1 neurons were observed in the untreated G7 (G7–Dox) mouse. Scale bars are given in µm.