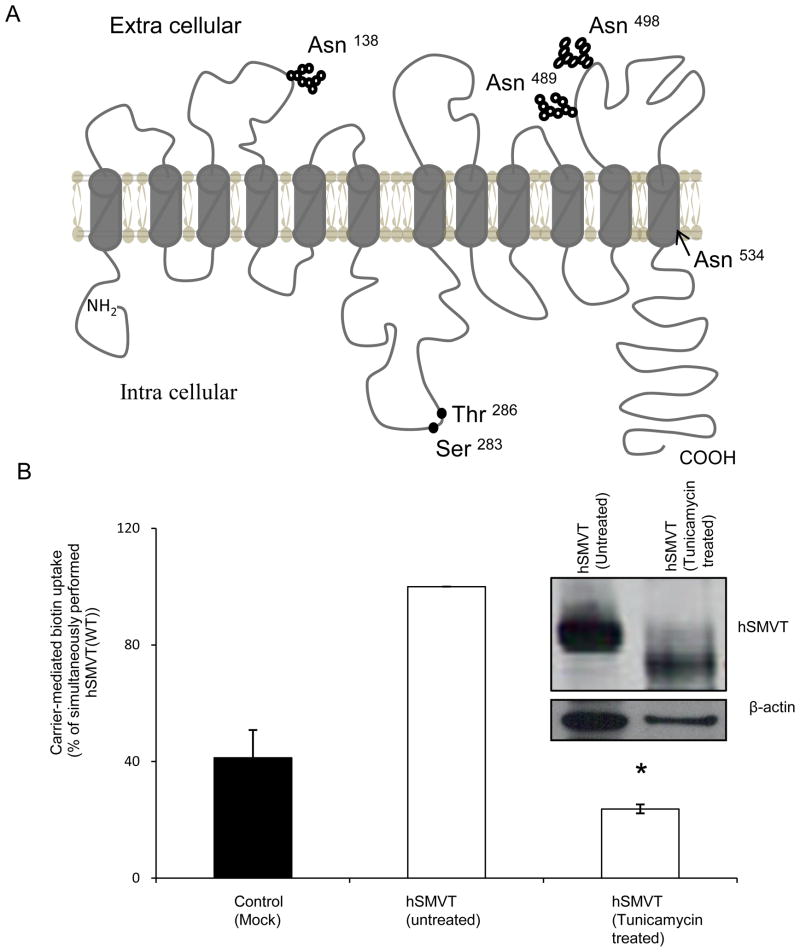
Fig. 1. hSMVT protein is glycosylated, and glycosylation is important for function.
A: Predicted membrane topology of hSMVT. Theoretical prediction suggests the hSMVT protein to have 12 TMD [11, 13]. The protein is also predicted to have four putative N-glycosylation motifs (Asn138, Asn489 Asn498 and Asn 534) and two potential PKC-phosphorylation sites (Ser283 and Thr286). B: Effect of tunicamycin on carrier-mediated biotin uptake by ARPE19 cells transiently expressing hSMVT. Following pre-treatment with tunicamycin (2 μg/ml for 48 h) biotin uptake was assayed in KR buffer (pH 7.4). Control cells were transfected with empty pcDNA3.1(−) vector. Data are mean ± SE of three independent experiments. * p < 0.01. inset: Western blot showing a shift in the molecular mass of hSMVT-GFP upon tunicamycin pre-treatment. Transiently expressing ARPE19 cells were pre-treated with tunicamycin (2 μg/ml for 48 h) and total protein was isolated as described in “Methods”. Equal amount of protein (30 μg) was resolved in NuPAGE 4–12% Bis-Tris gradient mini gels and subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-GFP monoclonal antibody. As a control, the same blot was probed with anti- β-actin antibody. The image shown is a representative of three independent experiments.