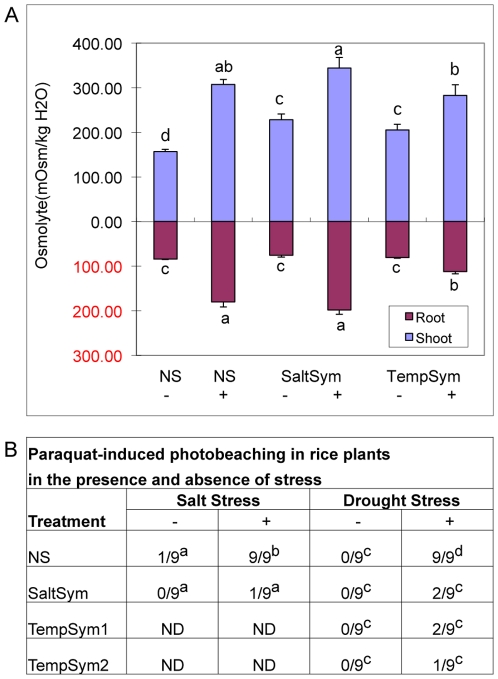
Figure 5. Effect of symbiosis on plant osmolyte concentrations and paraquat-induced photobleaching (ROS) under laboratory conditions.
A) Five week old rice plants (N = 30) that were NS or colonized with SaltSym or TempSym1 exposed for ten days in the absence (-) and presence (+) of salt stress (300 mM NaCl), at which point, the effects of stress began to show in NS plants treatments (≥70% wilted +/−chlorosis). SaltSym imparts salt tolerance and TempSym1 does not. Osmolyte concentrations (milliosmoles per kg wet weight) of roots and shoots were assessed and statistical analysis (Duncan's multiple-range test; SE≤9.98 &<23.73 for root, and shoot, respectively; P<0.0001 for root and shoot) indicated significantly higher levels in the shoots of S plants compared to NS plants in the absence of salt stress, and no statistical differences between treatments in the presence of salt stress. No significant differences were observed in roots in the absence of salt stress. In the presence of stress, Tempsym1+ showed significantly lower level of osmolytes than SaltSym+ and NS+ treatments. Values with the same letters are not significantly different. B) NS and S (SaltSym and TempSym1 & 2) plants exposed to salt (300 mM NaCl, 10 days) and drought stress (3 days) were tested for paraquat-induced photobleaching (ROS activity). Time points were chosen when symptoms began to appear (wilting and chlorosis) in NS stressed plants. Leaf disks (N = 9) from 9 independent plants were used for ROS assays. Leaf disks were sampled from leaf tissues of similar size, developmental age, and location for optimal side-by-side comparisons. Values indicate the number of leaf disks out of a total of nine that bleached white after exposure to paraquat indicating ROS generation. Statistical analysis (Duncan's multiple-range test) indicated that in the absence of stress, little to no (0–11%) photo beaching occurred in all the treatments. In contrast, significant differences occurred with 100% of the NS plant disks for both salt and drought stress bleaching white compared to only 11–22% of the S plant disks (P<0.0001). ND = not determined.