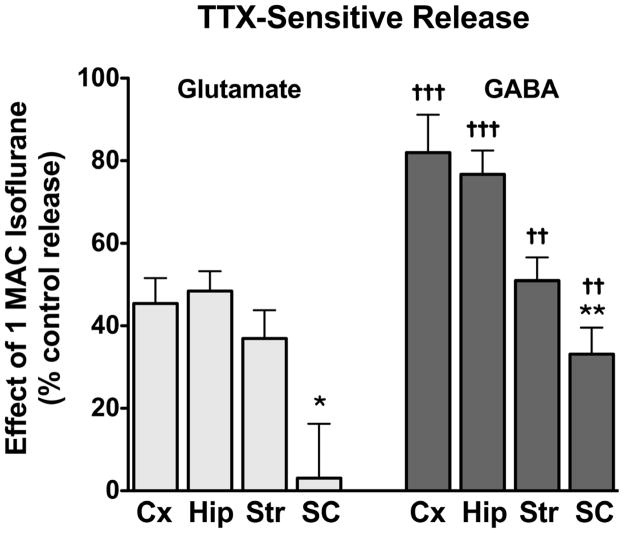
Figure 6.
Inhibition by isoflurane of tetrodotoxin-sensitive 4AP-evoked glutamate and GABA release. The effects of isoflurane at 1 MAC on TTX-sensitive 4AP-evoked release from cortical (Cx, 0.36 ± 0.03 mM isoflurane, n = 8), hippocampal (Hip, 0.36 ± 0.03 mM isoflurane, n = 8), striatal (Str, 0.35 ± 0.09 mM isoflurane, n = 8), and spinal cord (SC, 0.35 ± 0.04 mM isoflurane, n = 16) nerve terminals were determined by subtracting release in the presence of 1 μM TTX from release at the same concentration of isoflurane in the absence of TTX (see Methods for details). Inhibition by isoflurane of TTX-sensitive glutamate and GABA release from the same preparations of nerve terminals (mean ± SEM) were compared by paired t-tests (††P < 0.01; †††P < 0.001). Comparisons between CNS regions (***P < 0.001), (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA.