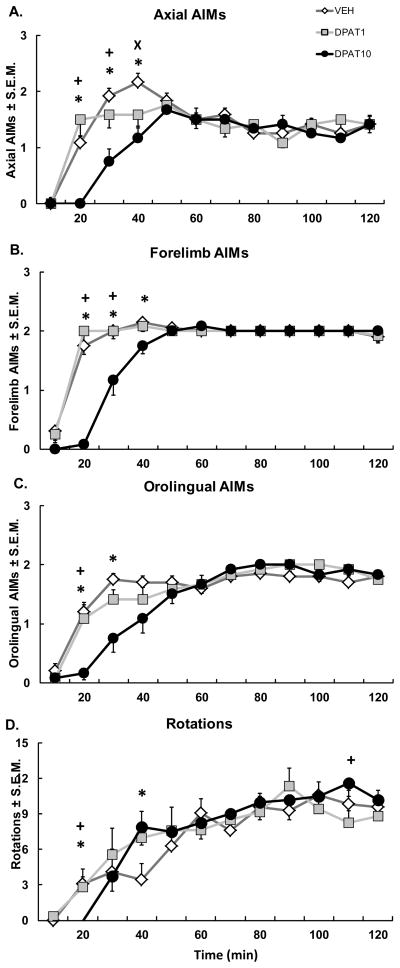
Figure 3. Intracortical ±8-OH-DPAT attenuates onset of ALO AIMs subtypes.
Five min after intracortical microinfusions of Vehicle (VEH) or the 5-HT1AR agonist ±8-OH-DPAT (DPAT; 1 or 10 μg), DA depleted rats received systemic injections of L-DOPA + Benserazide (12 + 15 mg/kg, sc). Graphs depict the treatment means for (A) Axial, (B) Forelimb, and (C) Orolingual AIMs ± S.E.M., as well as (D) Rotations ± S.E.M. for 6-OHDA-lesioned rats over 2 hr of observation. Treatment effects were analyzed with Friedman ANOVAs for Axial, Forelimb, and Orolingual AIMs and two-way repeated-measures ANOVAs for Rotations. Post hoc comparisons denote significant differences between treatments at the time points indicated (*p < 0.05 for DPAT10 vs. VEH; ×p < 0.05 for DPAT1 vs. VEH; +p < 0.05 for DPAT10 vs. DPAT1).