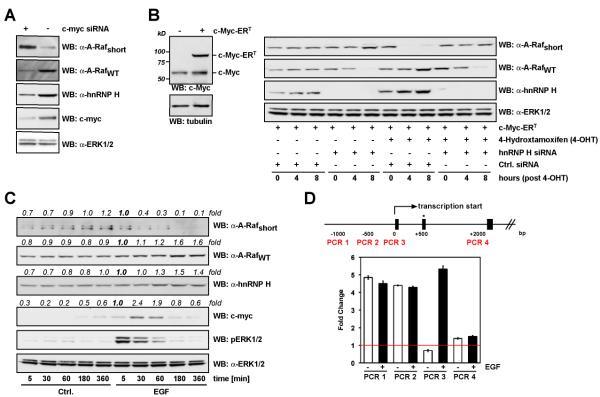
Figure 5: c-Myc regulates hnRNP H expression.
(A) Hela cells were transfected with either c-myc siRNA or control siRNA. Lysates were immunoblotted for expression of c-Myc, hnRNP H, A-RafWT or A-Rafshort, and ERK1/2 using specific antibodies. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with the 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT)-inducible chimeric MycERT, hnRNP H siRNA, or Control siRNA as indicated. Following transfection, cells were serum-starved for 16 hours (0.1% FCS) and MycERT induced with 4-OHT (100nM). 0, 4, and 8 hours post induction, cells were lysed and lysates immunoblotted for expression of the hnRNP H, A-RafWT or A-Rafshort, and ERK1/2 as loading control. (C) HeLa cells were serum-starved for 18 hours (0.1% FCS) and stimulated with EGF (10nM) as indicated. 5, 30, 60, 180, and 360min post stimulation, cells were lysed and lysates immunoblotted for expression of the c-Myc, hnRNP H, A-RafWT, A-Rafshort, phopho-ERK1/2, and ERK1/2 as loading control. (D) c-Myc binds to promotor elements of the human HNRNPH1 genomic locus. c-Myc Chromatin IPs in either serum-starved (18hrs, 0.1% FCS) or EGF-stimulated Hela cells were analyzed using semi-quantitative Real-time PCR. PCR primer pairs correspond to elements in the human hnRNP H promotor region as depicted. The red line indicates no change in c-Myc-specific enrichment. Shown are the representative results from three independent experiments, error bars represent standard deviations.