Fig. 1.
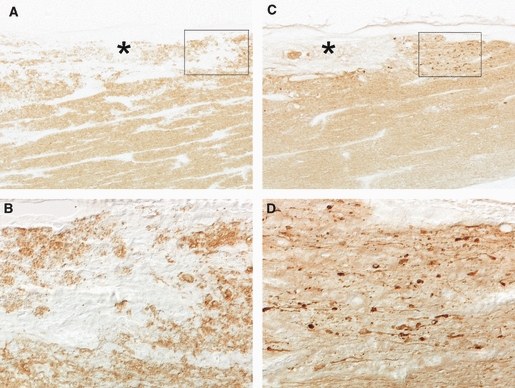
Oligodendroglial and axonal damage occurs after inhibition of glutamate transport in optic nerve. (A, B) Glutamate transporter blocker dihydrokainate induces local demyelination (*) as revealed by immunostaining with antibodies to myelin basic protein. (B) is a higher-magnification of the inset in (A). (C, D) Immunohistochemistry with antibodies to dephosphorylated neurofilaments shows axonal loss in demyelinated areas (*) and severe axonal dystrophy in nearby regions after glutamate transport inhibition. (D) Higher-magnification of inset in (C), illustrating the swelling characteristics of axonal damage. Modified from Domercq et al. (2005).
