Fig. 6.
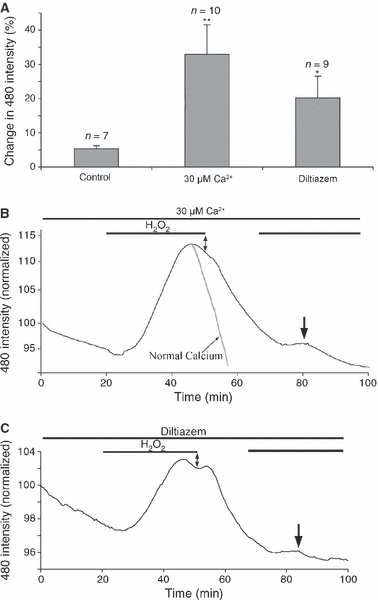
Rapid ROS buffering is partly Ca2+-dependent. (A) Mean change in DCF fluorescence in normal Ca2+, 30 μm Ca2+, and in the presence of the Ca2+ channel blocker diltiazem (50 μm). *P < 0.05 vs. control, **P < 0.01 vs. control. (B) The mean change in DCF fluorescence for nerves exposed to 100 μm H2O2 in 30 μm Ca2+. Note that the fluorescence remains elevated in the continued presence of H2O2 (double arrow), and the response to a second exposure to H2O2 (arrow). The mean decline in normal Ca2+ is included for comparison, scaled to match (grey trace). (C) Similar plot for the mean DCF changes evoked by 100 μm H2O2 in the presence of diltiazem.
