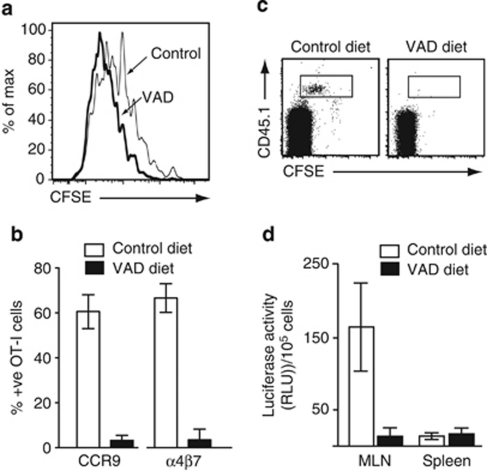
Figure 1.
Vitamin A is essential for induction of CC chemokine receptor (CCR)9 and α4β7 on activated T lymphocytes in vivo. (a–c) OT-I.CD45.1 cells were adoptively transferred into CD45.2 long-term vitamin A-deficient (VAD) mice or control mice. (a) CFSE dilution and (b) CCR9 and α4β7 expression on responding OT-I cells in the mesenteric lymph node (MLN) of mice kept on a conventional (white bar) or long-term VAD (black bar) diet 3 days after oral ovalbumin (OVA) administration. Results are (a) representative FACS plots from three experiments with two to three mice per group per experiment and (b) mean (s.d.) of four experiments with two to three mice per group per experiment. (c) FACS plots of CD8+ intraepithelial lymphocytes in long-term VAD and control mice 3 days after OVA administration. Representative results from one experiment of three with two to three mice per group per experiment. (d) DR5.OT-I cells were adoptively transferred into CD45.1 long-term VAD or control mice. OVA and LPS were injected i.p., and 1 day later, mice received FTY720 to prevent OT-I.DR5 cell egress from secondary lymphoid organs. OT-I cells were sorted 3 days after immunization and assessed for luciferase activity. Results are the mean (s.d.) of three experiments, two to four mice per group per experiment. CFSE, carboxyfluorescein; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; i.p., intraperitoneal; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; RLU, relative luciferase units.