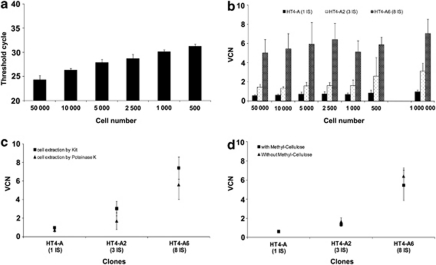
Figure 2.
Determination of VCN by Q-PCR. (a) The sensitivity of the Q-PCR was evaluated by measuring CT values (average of duplicate measures) for the amplification of the albumin gene sequences in decreasing numbers of control cells. Q-PCR was carried out from 1/6 of the total genomic DNA extracted from 500–50 000 cells. (b) VCN in the HT4-A, HT4-A2 and HT4-A6 clones were measured after proteinase K lysis extractions of separate preparations of cells ranging from 500–50 000 cells per condition. The Q-PCR was performed on 1/6 of the extracted genomic DNA as in Figure 2a. The control indicated on the right side of the graph corresponds to Q-PCR on genomic DNA obtained from 1 × 106 cells extracted with a commercial Promega kit. (c) Comparison of VCN values obtained on the three clones using genomic DNA extracted either by proteinase K lysis from a number of cells inferior to 5 × 104 or using a commercial kit and 1 × 106 cells per extraction. (d) Comparison of VCN values obtained by Q-PCR from the three clones using genomic DNA extracted by proteinase K lysis in the presence (5 μl per condition) or absence of methylcellulose.