Abstract
Terrestrial arthropods, at constant risk from desiccation, are highly sensitive to atmospheric temperature and humidity. A physiological marker of these abiotic conditions could highlight phenotypic adaptations, indicate niche partitioning, and predict responses to climate change for a group representing three-quarters of the Earth's animal species. We show that the 18O composition of insect haemolymph is such a measure, providing a dynamic and quantitatively predictable signal for respiratory gas exchange and inputs from atmospheric humidity. Using American cockroaches (Periplaneta americana) under defined experimental conditions, we show that insects respiring at low humidity demonstrate the expected enrichment in the 18O composition of haemolymph because of evaporation. At high humidity, however, diffusional influx of atmospheric water vapour into the animal forces haemolymph to become depleted in 18O. Additionally, using cockroaches sampled from natural habitats, we show that the haemolymph 18O signature is transferred to the organic material of the insect's exoskeleton. Insect cuticle, therefore, exhibits the mean atmospheric conditions surrounding the animals prior to moulting. This discovery will help to define the climatic tolerances of species and their habitat preferences, and offers a means of quantifying the balance between niche partitioning and ‘neutral’ processes in shaping complex tropical forest communities.
Keywords: stable isotopes, arthropods, niches, neutral theory, climate change
1. Introduction
In the face of global environmental change there is an urgent need to understand the rules governing the structure of ecological assemblages, and for unequivocal, quantitative evidence for the effects of climate disruption on the structure and dynamics of threatened communities [1]. At present, we lack a comprehensive understanding of the organization of ecosystems such as tropical forests, and of their gaseous exchanges with the atmosphere, which limits attempts to predict the responses of these ecosystems to climate change [2]. Stable isotopes, widely used to answer intricate physiological and ecological questions in a variety of organisms [3], offer an elegant solution.
Insects and other tracheated arthropods, which make up three-quarters of all animal species [4], show a strong response to moisture gradients in tropical forests [5]. These animals respire through a series of spiracles, the tracheal openings which allow air to diffuse into the animal while optimizing gas exchange and controlling respiratory water loss [6]. As water evaporates, the lighter isotope (16O) changes phase and diffuses more rapidly than the heavier isotopomer (containing 18O). As a result, water vapour is depleted in 18O by around 10 parts per thousand (‰), whereas liquid water at the site of evaporation becomes enriched in 18O. The extent of 18O enrichment is controlled by the bidirectional exchange of water vapour between the surface of water bodies and the atmosphere, and is therefore a function of temperature and relative humidity (RH), as described by the Craig–Gordon equation [7].
Here, we demonstrate experimentally that the 18O signal of insect haemolymph in American cockroaches (Periplaneta americana) shows evaporative enrichment at low humidity, whereas under high humidity, there is an influx of 18O-depleted water vapour into the animal. Furthermore, the distinct signal correlating high humidity and water vapour uptake was present in the chitin of cockroaches from a range of natural habitats and contrasting global distributions.
2. Material and methods
At the start of the experiment, 14 adult male cockroaches were placed into each of eight plastic chambers. Initial haemolymph δ18O for these cockroaches was +2‰ versus Standard Mean Oceanic Water (SMOW) international isotopic standard, enriched compared with local tap water inputs (−8‰ versus SMOW) because of the low humidity (50% RH) in the controlled environment room. On days 2, 4 and 6, three cockroaches were removed from each chamber (the remaining five cockroaches were removed on day 8).
Water vapour was generated from two water sources, one ‘enriched’ in 18O (δ18O = −8‰: local, UK, tap water), the other relatively ‘depleted’ (δ18O = −12‰: Vienna, Austria, tap water). Two ambient RHs (98 and 50%) were derived by sparging air at 300 ml min−1 through samples of each water source, maintained either at 30°C (saturated vapour pressure 3.71 kPa, to derive 98% RH) or 10°C (saturated vapour pressure 1.25 kPa, to derive 50% RH at the experimental chamber temperature). Half of the cockroaches (one set of four chambers) were provided with unlimited access to local, UK, tap water, δ18O = −8‰. Water consumption was measured daily using pipettes modified with a lateral orifice to allow insects to remove water ad libitum. In the second set of four chambers, cockroaches did not have access to drinking water.
Haemolymph δ18O analysis was conducted indirectly by equilibrating a known concentration of CO2 in the headspace of an Exetainer with 0.2 ml liquid for 3 days at 20°C, prior to purification and mass spectrometric analysis (VG Sira 10 Isotope ratio mass spectrometer). The precise δ18O of Cambridge and Vienna water was −8.41 ± 0.26‰ and −12.49 ± 0.21‰ versus SMOW, and the δ18O of water vapour generated from each source was −18.23 ± 0.27‰ (Cambridge) and −22.41 ± 0.38‰ (Vienna) versus SMOW. The equilibration and purification procedure were standardized on a daily basis against CO2 equilibrated with a tap water laboratory standard and calibrated overall against two secondary standards [British Antarctic Survey (BAS) low and BAS high, respectively, −31.44 and −8.73‰ versus SMOW]. Chitin δ18O analysis was completed on bulk samples from the hind tibia of five conspecific adult male cockroaches per habitat using a Thermo Finnigan 253 with TC (High Temperature Conversion) Elemental Analyser (Godwin Laboratory, University of Cambridge, UK) calibrated against NBS 127 and SMOW. These wild cockroaches were collected from two habitats per geographical location, preserved in alcohol and then dried.
To model the data, we used a parametrized non-steady state (NSS) version [8] of the Craig–Gordon enrichment equation (cf. equations 4 and 5 in Seibt et al. [8]). The NSS model integrates 18O enrichment as a function of time and rate of (leaf) tissue-water turnover—or in this case—turnover of the cockroach haemolymph. Starting with the initial (control) δ18O of insect haemolymph for each treatment, the model was parametrized with the respective δ18O of water vapour, temperature, RH and measured weight change in each insect for the next 2 day sampling period. The NSS model was used to predict the haemolymph δ18O for that subsequent period, and for each successive sampling period.
3. Results
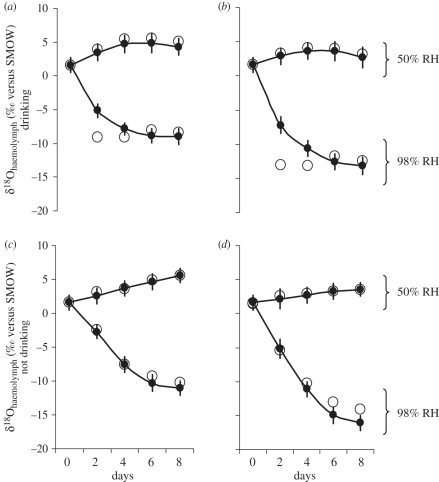
At low humidity (50% RH), both the measured data and the NSS model showed isotopic enrichment occurring in haemolymph through respiration and evaporative water loss (figure 1). However, at high atmospheric humidity (98% RH), water vapour uptake during respiration by P. americana reset the isotopic composition of the haemolymph, which became depleted (δ18O more negative) as the influx of water vapour dominated the water budget of the insect (figure 1).
Figure 1.
Effect of relative humidity (RH) and water vapour on the 18O composition of the haemolymph of P. americana. (a) With drinking water at 50 versus 98% RH, while breathing enriched vapour at −18‰ from local UK tap water; (b) with drinking water at 50 versus 98% RH, while breathing depleted vapour at −22‰ from Vienna tap water; (c) without drinking water at 50 versus 98% RH, while breathing enriched vapour at −18‰ from local UK tap water; and (d) without drinking water at 50 versus 98% RH, while breathing depleted vapour at −22‰ from Vienna tap water (filled circles, observed; open circles, predicted).
In cockroaches with access to drinking water, there was a delay in the isotopic depletion of the haemolymph compared with the model, but after six days there was an agreement between modelled and observed values, with δ18O decreasing to −9‰ in those cockroaches breathing enriched vapour (i.e. −1‰ below the 18O composition of the drinking water; figure 1a), and −13‰ in the cockroaches breathing depleted vapour (i.e. −5‰ below the 18O composition of the drinking water; figure 1b).
In cockroaches without access to drinking water, there was close agreement between observed and modelled values: after eight days δ18O decreased to −11‰ in the cockroaches under enriched vapour, and to −16‰ in the cockroaches breathing depleted vapour (figure 1c,d). Interestingly, it seems that water vapour uptake and condensation can occur beyond normal equilibrium exchange, as seen by the decrease in haemolymph δ18O below the value predicted by the model (figure 1d).
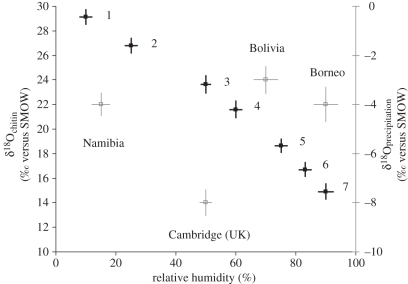
We compared the chitin from P. americana used experimentally with cockroach species collected from a variety of natural habitats, including the internal chambers of an epiphytic bird's nest fern (Asplenium nidus) in lowland tropical forest in Borneo [9]. There were significant differences in the 18O composition of all species (one-way ANOVA: F6,28 = 35.51, n = 35, p < 0.001; figure 2). Most striking was the highly significant correlation between the depletion of 18O in insect chitin and increasing RH (Pearson's r = −0.989, p < 0.001; solid symbols, figure 2). This relationship is apparent for both RH measured at the point of collection of each species (solid symbols, figure 2), and mean local RH calculated for the date of collection from the local air temperature and vapour pressure [10] (open symbols, figure 2). By contrast, the 18O signatures of local precipitation likely to be ingested by the cockroaches [10] showed no significant relationship with the 18O signature of cockroach chitin (Pearson's r = −0.137, p = 0.769; figure 2).
Figure 2.
Effect of RH on the 18O composition of the chitin of cockroaches from natural habitats. Solid points show, in ascending order of latitude, the 18O composition and the within-habitat RH for: (1) Namablatta bitaeniata and (2) Tivia sp. from the Brandberg, Swakopmund District, Namibia, 21°9′ S, 14°35′ E; (3) Periplaneta americana, our model insects, which were grown in controlled environment chambers in Cambridge, UK; (4) Ischnoptera sp. and (5) Epilampra sp. from the Refugio Los Volcanes, Santa Cruz, Bolivia, 18°06′ S, 63°36′ W; (6) Margatta sp. and (7) Haania sp. from inside an epiphytic bird's nest fern in Danum Valley, Sabah, Borneo, 4°58′ N, 117°48′ E (mean ± s.e., n = 5 cockroaches). Open points show the 18O composition of the precipitation, and the mean local RH, at each location (mean ± s.e., n = 5 recordings).
4. Discussion
Insect haemolymph represents an isolated pool of water, and hence the 18O isotopic composition can be defined by the Craig–Gordon model [7], which incorporates kinetic and equilibrium isotope transformations driven by temperature and humidity. Although the NSS version used in this paper was developed for use in plants [11], we hypothesized that short-term disequilibria in daily plant-water supplies and stomatal apertures might be equivalent to intermittent drinking and discontinuous gas exchange in insects [6], thus allowing the extent of water vapour uptake at high humidity to be tracked (cf. Helliker & Griffiths [11]). Source precipitation or ground-water determines the starting point for plant tissue-water and insect haemolymph signals, refined by temperature and humidity (see progression in figure 1). The integration of daily mean humidity is then transferred isotopically into the chitin (C8H13O5N), together with a systematic (and constant) enrichment factor when the insect moults [12], as we have shown for individual cockroaches from natural habitats, including those specifically associated with epiphytic bird's nest ferns in a rainforest canopy in Borneo (figure 2). Arthropods of this particular forest show a strong response to temperature and moisture gradients [5], which are a common feature of tropical forest canopies, often being associated with vertical stratification [2]. However, bird's nest ferns buffer microclimatic fluctuations [13], and provide discrete habitats for their invertebrate inhabitants [9]. We therefore propose that the 18O signals in terrestrial arthropods can be used to integrate species distributions with microclimate and climate change [14], and that natural microcosms such as epiphytes offer the prospect for determining the extent to which niche partitioning, as compared with ‘neutral’ processes, shape complex tropical forest communities [15].
The experimental data show the interplay between source-water inputs and atmospheric humidity for insects: under low humidity, evaporative enrichment occurs, but under high humidity the ingested water δ18O signal is reset by the isotopically depleted vapour influx (figure 1a,b), despite net evaporation of haemolymph (see the electronic supplementary material results and figure S1). Accordingly, the δ18O of haemolymph was lower than that of drinking water by up to 5‰, particularly in those cockroaches breathing depleted vapour (−8‰ versus −13‰; figure 1b). This helps to explain the lack of correlation between the 18O signals in cockroach chitin and local precipitation in South America, Africa and Borneo (figure 2), also seen in other studies [12].
With regard to the depletion of haemolymph δ18O below that predicted by the model (figure 1d), it is possible that condensation is occurring inside the tracheoles, where water vapour might not be at isotopic exchange equilibrium with the external atmosphere. Thus, when spiracles are closed, a Rayleigh distillation [16] could lead to the progressive condensation of lighter isotopes—similar to that seen in clouds with altitude—which would lead to progressive depletion of residual water vapour within the tracheoles, and haemolymph signals that are more depleted than predicted by the model. Meanwhile, whether there are isotopic shifts associated with water vapour absorption [17], or with fluid reabsorption by the Malpighian tubules [18], and whether the haemolymph of insects with contrasting life cycles responds in the same way as in cockroaches, has yet to be resolved.
Acknowledgements
The Departments of Zoology and Plant Sciences, University of Cambridge, supported this work. Darren Mann of the Oxford University Museum of Natural History kindly donated cockroach specimens. M.D.F.E. is grateful to Daphne Ellwood for her support and to Michael Akam, Adrian Friday and Simon Maddrell for their valuable discussion.
References
- 1.Pimm S. L. 2009. Climate disruption and biodiversity. Curr. Biol. 19, 595–601 10.1016/j.cub.2009.05.055 (doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.05.055) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ozanne C. M. P., et al. 2003. Biodiversity meets the atmosphere: a global view of forest canopies. Science 301, 183–186 10.1126/science.1084507 (doi:10.1126/science.1084507) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.West J. B., Bowen G. J., Cerling T. E., Ehleringer J. R. 2006. Stable isotopes as one of nature's ecological recorders. Trends Ecol. Evol. 21, 408–414 10.1016/j.tree.2006.04.002 (doi:10.1016/j.tree.2006.04.002) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stork N. E. 1988. Insect diversity: facts, fiction and speculation. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 35, 321–337 10.1111/j.1095-8312.1988.tb00474.x (doi:10.1111/j.1095-8312.1988.tb00474.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dial R. J., Ellwood M. D. F., Turner E. C., Foster W. A. 2006. Arthropod abundance, canopy structure, and microclimate in a Bornean lowland tropical rain forest. Biotropica 38, 643–652 10.1111/j.1744-7429.2006.00181.x (doi:10.1111/j.1744-7429.2006.00181.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schimpf N. G., Matthews P. G. D., Wilson R. S., White C. R. 2009. Cockroaches breathe discontinuously to reduce respiratory water loss. J. Exp. Biol. 212, 2773–2780 10.1242/jeb.031310 (doi:10.1242/jeb.031310) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Craig H., Gordon L. 1965. Deuterium and oxygen 18 variations in the ocean and marine atmosphere. In Stable isotopes in oceanographic studies and paleotemperatures (ed. Tongiorigi E.), pp. 9–130 Pisa, Italy: Consiglio Nazionale Delle Ricerche Laboratorio di Geologia Nucleare [Google Scholar]
- 8.Seibt U., Wingate L., Berry J. A., Lloyd J. 2006. Non-steady state effects in diurnal 18O discrimination by Picea sitchensis branches in the field. Plant Cell Environ. 29, 928–939 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01474.x (doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01474.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ellwood M. D. F., Foster W. A. 2004. Doubling the estimate of invertebrate biomass in a rainforest canopy. Nature 429, 549–551 10.1038/nature02560 (doi:10.1038/nature02560) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.IAEA/WMO 2006. Global network of isotopes in precipitation. The GNIP database. See http://www.iaea.org/water
- 11.Helliker B. R., Griffiths H. 2007. Toward a plant-based proxy for the isotope ratio of atmospheric water vapour. Global Change Biol. 13, 723–733 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01325.x (doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01325.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schimmelmann A., DeNiro M. J. 1986. Stable isotopic studies on chitin. III. The D/H and 18O/16O ratios in arthropod chitin. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 1485–1496 10.1016/0016-7037(86)90322-4 (doi:10.1016/0016-7037(86)90322-4) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Turner E. C., Foster W. A. 2006. Assessing the influence of bird's nest ferns (Asplenium spp.) on the local microclimate across a range of habitat disturbances in Sabah, Malaysia. Selbyana 27, 195–200 [Google Scholar]
- 14.McGill B. J. 2010. Matters of scale. Science 328, 575–576 10.1126/science.1188528 (doi:10.1126/science.1188528) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ellwood M. D. F., Manica A., Foster W. A. 2009. Stochastic and deterministic processes jointly structure tropical arthropod communities. Ecol. Lett. 12, 277–284 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2009.01284.x (doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2009.01284.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Scott K. M., Lu X., Cavanaugh C. M., Liu J. S. 2004. Optimal methods for estimating kinetic isotope effects from different forms of the Rayleigh distillation equation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 68, 433–442 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00459-9 (doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00459-9) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.O'Donnell M. J. 1977. Site of water vapor absorption in the desert cockroach, Arenivaga investigata. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 74, 1757–1760 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1757 (doi:10.1073/pnas.74.4.1757) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.O'Donnell M. J., Maddrell S. H. P. 1995. Fluid reabsorption and ion transport by the lower Malpighian tubules of adult female Drosophila. J. Exp. Biol. 198, 1647–1653 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]