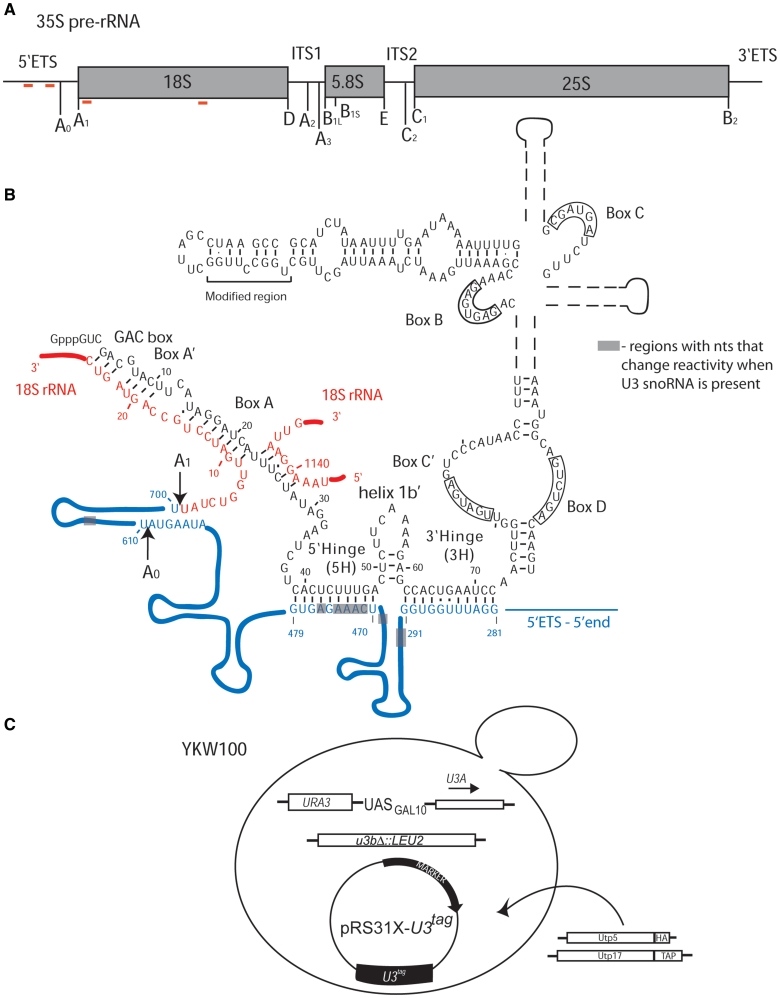
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic of the 35S primary pre-rRNA transcript in S. cerevisiae with the processing sites indicated. The 35S pre-rRNA is composed of the 18S, 5.8 and 25S rRNAs, separated by the internal transcribed spacers (ITS1 and ITS2) and the two external transcribed spacers (5′-ETS and 3′-ETS). The red lines indicate the base pairing sites for the U3 snoRNA. (B) The secondary structure of the U3 snoRNA base paired to the 35S pre-rRNA adapted from ‘The Yeast snoRNA database’ (43) and Mereau et al. (14). The U3 snoRNA is shown in black and its different structural and functional elements are indicated, including the modified region used for detection by northern blotting. The 5′-ETS region of the 35S pre-rRNA is shown in blue, the 18S rRNA is shown in red and the cleavage sites are indicated. The gray boxes indicate regions where nucleotides change reactivity to DMS when U3 snoRNA is present. The U3 snoRNA, 5′-ETS and the shaded boxes are not drawn to scale. (C) The YKW100 strain used to analyze the role of the U3 snoRNA in pre-rRNA folding. In the haploid S. cerevisiae strain YKW100 the U3B (SNR17b) gene is disrupted, while the U3A (SNR17a) is under the control of a galactose-inducible/dextrose repressible promoter (GAL10). Tagged U3 snoRNAs, wild-type or mutant, were expressed from plasmids carrying either TRP1 (pRS314) or HIS3 (pRS313) auxotrophic markers. For the co-immunoprecipitation experiments, Utp5 was HA-tagged (KANR) and Utp17 was TAP-tagged (TRP1).