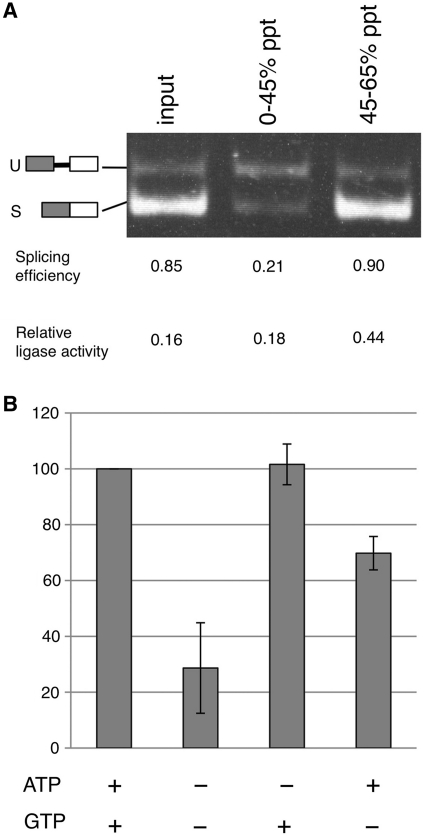
Figure 2.
Nucleotide requirements for the ligase activity. (A) To remove nucleotides from the rabbit erythrocyte lysate (REL) and partially purify the ligase for XBP1u mRNA splicing, we performed ammonium sulfate precipitation. REL was first saturated to 45% with ammonium sulfate and the protein precipitate (0–45% ppt) was collected by centrifugation. The resulting supernatant was then saturated to 65% with ammonium sulfate and the precipitate (45–65% ppt) was obtained by centrifugation. Each of these protein precipitates was dissolved in buffer A and dialyzed against the same buffer. The samples were then subjected to the splicing assay and their relative ligation activity was calculated as described in ‘Material and Methods’ section. U and S indicate the positions of the RT-PCR products representing the XBP1u and XBP1s RNAs. (B) After cleaving the XBP1u RNA with IRE1α, the cleaved product was purified and subjected to in vitro splicing reaction with the 45–65% fraction from the ammonium sulfate precipitation of REL. The activity observed in the presence of both 1.25 mM ATP and 0.75 mM GTP was taken as 100%. Error bars indicate standard deviations from the average of three independent experiments.