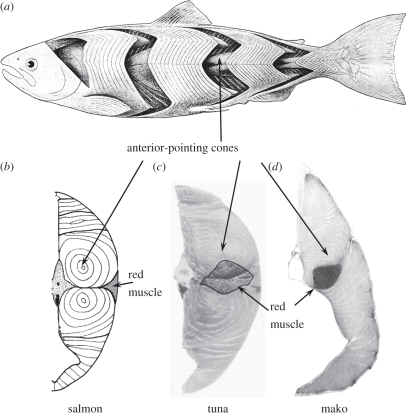
Figure 1.
(a) A diagram of a salmonid with skin removed to show the lateral muscle which contains two types of fibres, anaerobic white muscle and aerobic red muscle (modified from Greene & Greene [1]). White muscle is folded into a series of W-shaped segments called myomeres, one for each vertebra, with lateral posterior-pointing cones and medial anterior-pointing cones. These nested cones are seen as concentric rings in cross section (b). Tunas (c) and lamnid sharks (d) have elongated myomeres, so they have more rings. Red muscle sits just under the skin in non-thunniform fishes (b), but in tunas and lamnids it is found deep in the body, forming a loin at the anterior cones of the myomeres (c,d).