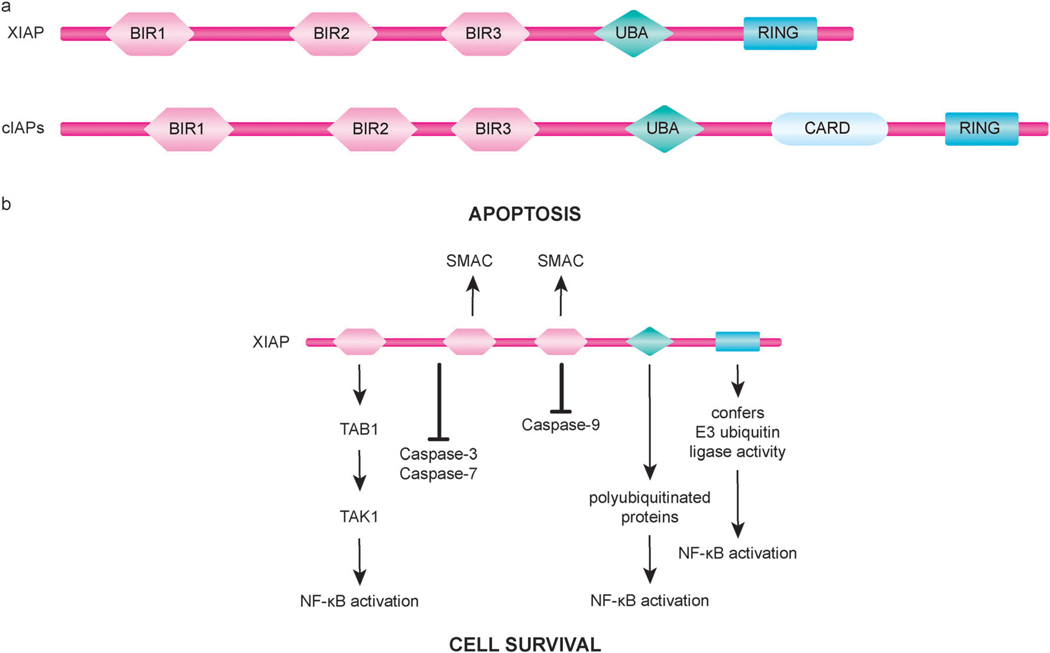
Fig. 3.
Domain organization and function of inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP) proteins. (a) XIAP, a well studied human IAP family member, and the structurally similar family members cIAP1 and cIAP2 (cIAPs) each have three tandem BIR domains followed by an ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain and a C-terminal RING finger domain. cIAPs also possess a caspase recruitment domain (CARD) of unknown function located between the UBA and the RING domains. (b) The BIR2 domain of XIAP, along with residues in its N-terminal flanking linker region, mediates the binding and inhibition of caspase-3 and caspase-7. Inactivation of caspase-9 by XIAP involves the BIR3 domain of XIAP binding to caspase-9. In addition to blocking caspase activity, XIAP can also promote cell survival through regulation of important cellular signaling pathways, including signaling mechanisms of NF-κB activation. IAP-binding motif (IBM)-containing proteins, such as SMAC, interact with the BIR2 and BIR3 domains of XIAP to neutralize its anti-apoptotic activity.