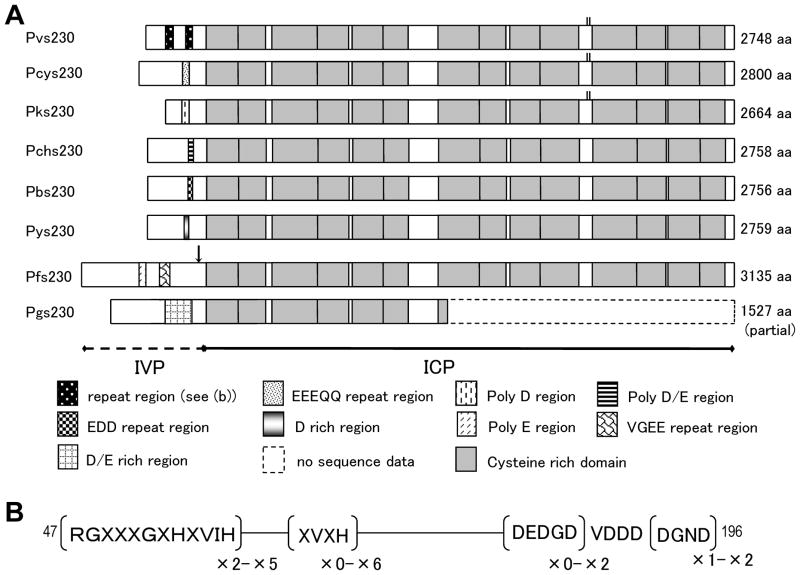
Fig. 1.
Primary structure of Pvs230 and its orthologs. In (a), deduced amino acid sequences obtained from P. vivax (Pvs230), P. cynomolgi (Pcys230), P. knowlesi (Pks230), P. chabaudi (Pchs230), P. berghei (Pbs230), P. yoelii (Pys230), P. falciparum (Pfs230), and partial sequence of P. gallinaceum (Pgs230: aa 1-1527) are aligned. In interspecies variable part (IVP), tandem repeat regions are represented as variously marked boxes, and 14 cysteine-rich domains in interspecies conserved part (ICP) are represented as half-tone boxes. Predicted cleavage sites of Pfs230 are marked by an arrow. Two cysteine residues between CRD10 and CRD11 in Pvs230, Pcys230 and Pks230 are shown in small bars. Predicted amino acid sizes are shown in right of respective amino acid sequences. In (b), repeat motifs and their repeat number in Pvs230 are shown, in which X denotes any amino acid residues. Major repeat units in RGXXGXHVIH are RGSYEGIHQVIH, RGRCEGIHQVIH, and RGRCDGGHHVIH, those in XVXH are RVVH, CVVH, RVAH, and RVIH (Suppl. Fig. 2). Amino acid positions are numbered after the Pvs230 sequence of Sal-1 strain (GenBank accession #XM_001612970).