Fig. 1. Reaction of allopurinol with XO induces ROS formation.
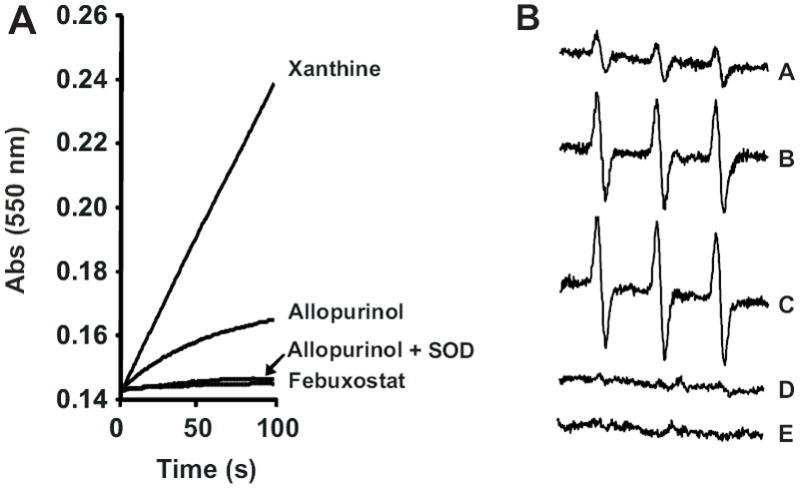
(A) XO (10 mU/ml) was exposed to either xanthine (50 μM), allopurinol (50 μM), Febuxostat (100 nM) or allopurinol (50 μM) + SOD (10 U/ml) and O2 •- formation monitored by the reduction of cytochrome c (λ = 550 nm) over time. (B) Xanthine oxidase (10 mU/ml) was exposed to allopurinol (50 μM) and O2 •- formation monitored by EPR spin trapping with PPH (100 μM). Spectra represent the following conditions: allopurinol 25, 50 and 100 s (A-C, respectively), 100 s + SOD (D) and 100 s + febuxostat (E).
