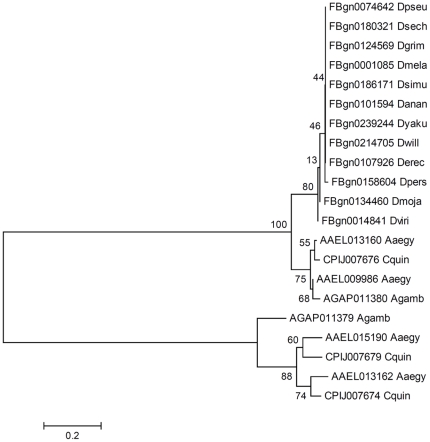
Figure 2. Evolutionary relationships of fz genes.
Relationships among orthologous mosquito and Drosophila Fz (Fz-1) proteins were inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method. The gene ID and the species name (5 letters) are shown for the orthologs. The optimal tree (the sum of branch length = 2.675) is shown. The percentage values of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together following bootstrap testing (1000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale (shown below the tree), with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogeny. The distance scale is in units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. The phylogenetic branching suggests that there could be an ancestral as well as a modern origin of mosquito fz genes in relation to Drosophila.