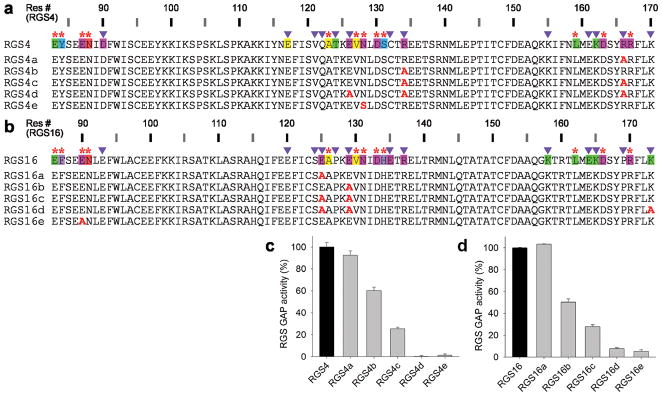
Figure 3.
Mutations in Modulatory positions impair the GAP activities of RGS4 and RGS16 in an additive manner. (a) Sequences of RGS4 mutations in Modulatory positions (RGS4a–d) and a Significant & Conserved position (RGS4e). (b) Sequences of RGS16 mutations in Modulatory positions (RGS16a–d) and a Significant & Conserved position (RGS16e). The annotated sequences of wild-type RGS4 and RGS16 in a and b are from Figure 2a. (c) GAP activities of RGS4 mutants determined by single turnover GTPase assays. 400 nM GTP-loaded Gαo was incubated with or without RGS4 (40 nM) for 1 min. GAP activities are expressed as a percentage of wild-type RGS4 activity. Experiments were conducted in triplicate with error bars representing s.e.m. (d) GAP activities of the RGS16 mutants, determined as in c.