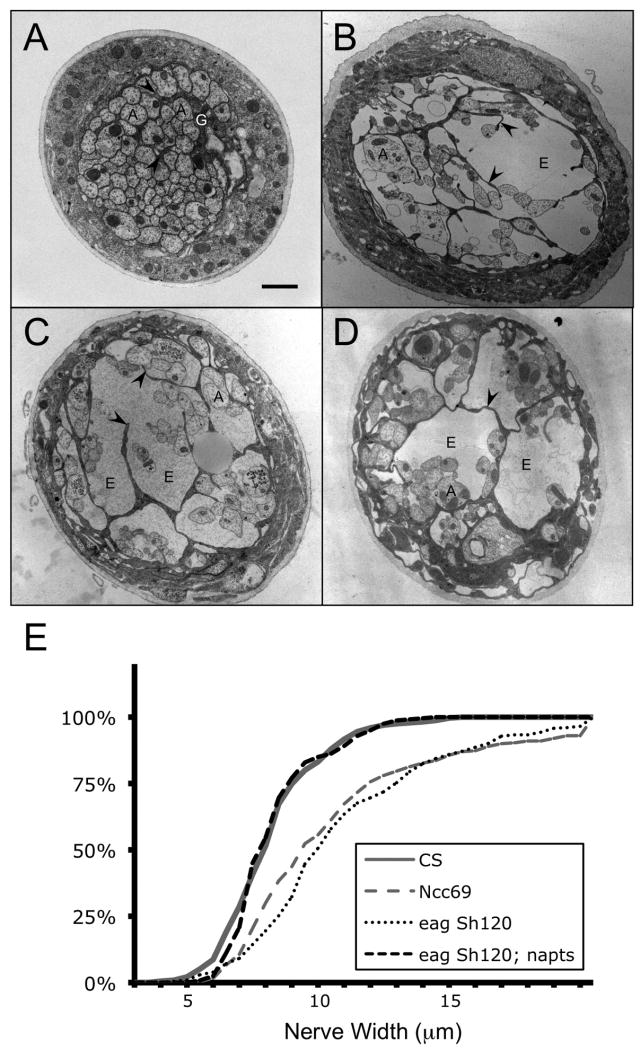
Figure 2.
Drosophila bulging nerve mutants. A-D: Transmission electron micrographs of nerves from 3rd instar larvae. In wild type A, axons (“A”) and glial cell processes (“G” and arrowheads) are closely associated, with little extracellular space. By contrast, in eag Sh B, Ncc69 C, and fray D mutant nerve bulges, axons and glia may be separated by a large amount of extracellular space (“E”). E. Cumulative frequency graphs of nerve widths. Curves from animals with a higher proportion of large nerve widths are shifted to the right; those with a lower proportion are shifted to the left. Both Ncc69 and eag Sh120 mutant larvae have larger nerve widths than wild type (CS). Introducing the mlenapts mutation into eag Sh120 suppresses neuronal hyperactivity and restores nerve widths to wild type levels. Bar in A: 1 micron; A-D are to the same scale. Genotypes: A, CS. B, eag Sh120. C, w; Ncc69r2. D, ry frayr1. E, eag Sh120; mlenapts.