Figure 4. Water-avoidance stress increases PGE2 hyperalgesia in gastrocnemius muscle.
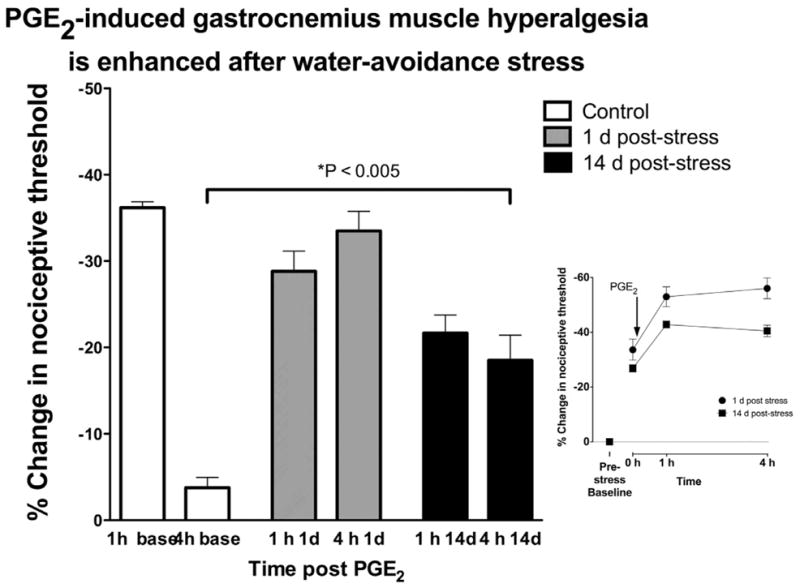
Mechanical hyperalgesia in the gastrocnemius muscle was measured 1 and 4 h after intramuscular administration of PGE2, in control (non-stressed) water-avoidance protocol exposed rats. In control, non-stressed rats, PGE2–induced decrease in mechanical nociception was present 1 h post injection, but had returned to near baseline at the 4 h time point. A similar PGE2 hyperalgesia was present in rats 1 d or 14 d after the last session of water avoidance stress (n=12). In water-avoidance stressed rats, the decrease in nociceptive threshold remained undiminished 4 h post PGE2 administration. Inset figure shows that exposure to water avoidance stress had a large effect on nociceptive threshold, decreasing it by 33.6% and 26.8% 1 and 14 day post-stress, respectively.
