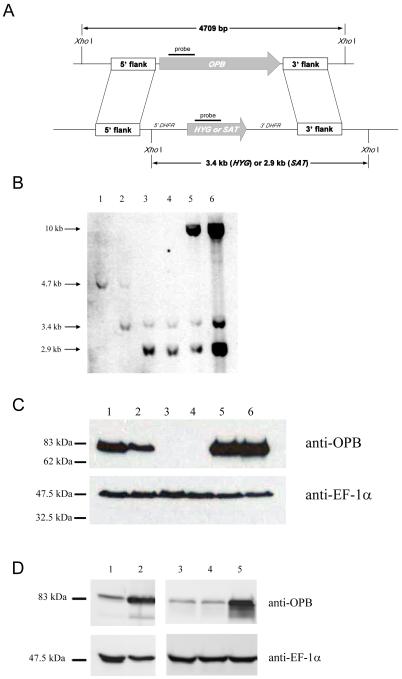
Fig. 2.
Deletion of L. major OPB.
A: Schematic representation of the OPB locus and the plasmid constructs used for gene replacement. The OPB and antibiotic resistance genes are shown as arrows, flanking DNA sequences are shown as boxes. XhoI fragments are shown. 5′-DHFR and 3′-DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase flanking regions; HYG, hygromycin resistance gene and SAT, streptothricin acetyltransferase resistance gene.
B: Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA digested with XhoI, separated on a 0.7% agarose gel, blotted onto a nylon membrane and hybridized using DNA probes corresponding to a 300 bp fragment of OPB, and the HYG and SAT genes. 1; L. major WT, 2; heterozygote, 3; Δopb clone 10, 4; Δopb clone 21, 5; Δopb clone 10 re-expressing OPB and 6; Δopb clone 21 re-expressing OPB. Molecular size markers are shown on the left.
C: Demonstration of OPB protein levels in L. major WT promastigotes and Δopb by western immunoblot. Lanes as in B. Purified anti-OPB antibody was used and EF-1α antibody as a loading control. A lysate of 5 × 106 cells was run in each lane.
D: Demonstration of over-expression of OPB in L. major cells by western immunoblot. Lane 1; L. major WT, 2; WT[OPB] population, 3; L. major WT, 4; WT[pNUS] population and 5; WT[OPBS577G] population. Purified anti-OPB antibody was used, with anti-EF-1α antibody as a loading control. A lysate of 5 × 106 cells was run in each lane.